Amazon Web Services Lambda support for Node.js
General support for AWS Lambda
Lambda services allow the execution of source code in the cloud. The execution can be set to be triggered by AWS events. Lambda functions can be deployed using several deployment frameworks. The supported deployment frameworks are listed on this page. When a lambda function is created and its runtime is Node.js, the Node.js extension is responsible for linking the Lambda objects and their triggers with the Java handler functions.
For example, consider source code that defines a Lambda function that has two triggers:
- an SQS queue
- an API Gateway
The Lambda function has a Nodejs runtime and the handler function is given by the handler function fullname. If the Lambda function is deployed using a supported deployment framework (such as CloudFormation ), the extension will create a Lambda function, an SQS receiver, and an API Gateway object. Each of these objects has a runtime property (Node.js) and a handler property with the function fullname. If the extension finds a JavaScript function matching the handler fullname, a link to that function will be added from the Lambda function, the SQS queue and the API Gateway object:
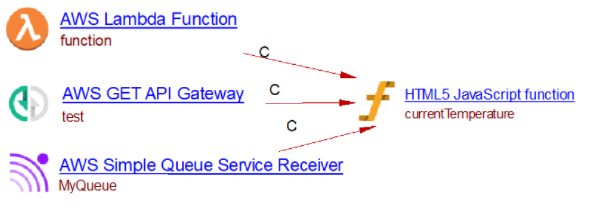
Lambda Invocation
A lambda can be executed through an invocation. A NodeJS Call to AWS Lambda Function object is then created. Its name is that of the invoked Lambda function. The com.castsoftware.wbslinker extension will then link that object to any matching Lambda objects.
Example
Code for SDK v2:
var AWS = require('aws-sdk');
// Set the region
AWS.config.update({region: 'REGION'});
AWS.config.credentials = new AWS.CognitoIdentityCredentials({IdentityPoolId: 'IDENTITY_POOL_ID'});
// Prepare to call Lambda function.
var lambda = new AWS.Lambda({region: 'REGION', apiVersion: '2015-03-31'});
var pullParams = {
FunctionName : 'Function_Name',
InvocationType : 'RequestResponse',
LogType : 'None'
};
function run() {
// Call the Lambda function
lambda.invoke(pullParams);
}
run();
Code for SDK v3:
const { LambdaClient } = require("@aws-sdk/client-lambda");
const { InvokeCommand } = require("@aws-sdk/client-lambda");
const REGION = "us-east-1";
const lambdaClient = new LambdaClient({ region: REGION });
export { lambdaClient };
const run = async () => {
// Set the parameters
const params = {
FunctionName: 'Function_Name', /* required */
ClientContext: 'STRING_VALUE',
InvocationType: Event | RequestResponse | DryRun,
LogType: None | Tail,
Payload: Buffer.from('...') || 'STRING_VALUE' /* Strings will be Base-64 encoded on your behalf */,
Qualifier: 'STRING_VALUE'
};
try {
const data = await lambdaClient.send(new InvokeCommand(params));
console.log("Success.", data);
return data; // For unit tests.
} catch (err) {
console.log("Error", err.stack);
}
};
run();
Either of the above code examples will produce the following results:
