JEE Analyzer - 2.0
Extension ID
com.castsoftware.jee
What’s new?
See JEE Analyzer - 2.0 - Release Notes.
Isofunctionality
This 2.x release of the extension is based on previous releases of the extension: see the Release Notes for more information. Note however, that the following support provided in previous releases of the extension has been removed from this release (and all future releases):
- The web client part of an application is no longer analyzed by this extension: specifically this means that JavaScript files and the JavaScript part of JSP pages will not be analyzed. In previous 1.x releases of this extension, these objects were analyzed by this extension and were materialized as “eFiles” in the analysis results. As a result of this change, your analysis results will differ in comparison to previous 1.x releases: there will be a change (a reduction) in LOC values due to the fact that eFile type objects that were previously created will no longer be created. Analysis of this code and the generation of associated objects is instead handled soley by com.castsoftware.html5 as was already the case in previous 1.x releases.
- Legacy environment profiles for Hibernate, Servlet, JSF and WBS have been removed.
Description
This extension provides support for analyzing applications built with JEE related technologies: objects and links between these objects are identified and Automated Function Point values are calculated. A set of JEE specific structural rules are also available with the extension.
Technology support
See Covered Technologies and also Technology support notes for additional information.
Function Point, Quality and Sizing support
| Function Points (transactions) | Quality and Sizing |
|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ |
CAST Imaging Core compatibility
| Operating System | Supported |
|---|---|
| Linux | ✅ |
Dependencies with other extensions
Some extensions require the presence of other extensions in order to function correctly. The JEE Analyzer extension requires that the following other extensions are also installed:
Note that any dependent extensions are automatically downloaded and installed for you. You do not need to do anything.
Download and installation instructions
For JEE applications, the extension will be automatically installed by CAST Imaging:
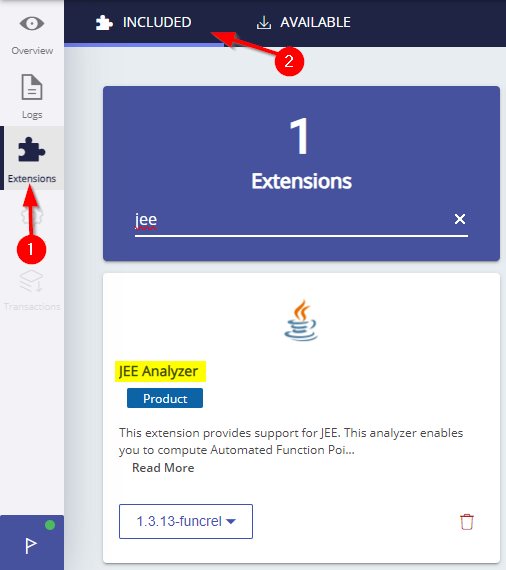
What analysis results can you expect?
Objects - Java
| Icon | MetaModel name |
|---|---|
 |
Generic Java Class |
 |
Generic Java Constructor |
 |
Generic Java Interface |
 |
Generic Java Method |
 |
Generic Java Type Parameter |
 |
Java Annotation Type |
 |
Java Annotation Type Method |
 |
Java Block |
 |
Java Class |
 |
Java Component |
 |
Java Constructor |
 |
Java Enum |
 |
Java Enum Item |
 |
Java Field |
 |
Java File |
 |
Java Import |
 |
Java Initializer |
 |
Java Instantiated Class |
 |
Java Instantiated Constructor |
 |
Java Instantiated Interface |
 |
Java Instantiated Method |
 |
Java Interface |
 |
Java Local Variable |
 |
Java Lambda Expression |
 |
Java Method |
 |
Java Package |
 |
Servlet |
 |
Servlet Mapping |
 |
Java Properties File |
 |
Java Property Mapping |
 |
J2EE XML File |
Objects - JSP (Presentation)
| Icon | MetaModel name |
|---|---|
 |
J2EE Scoped Bean |
 |
Servlet Attributes Scope |
 |
Bean Property |
 |
JSP EL Function |
 |
JSP File Template |
 |
J2EE XML Object |
 |
JSP Custom Tag |
 |
JSP Custom Tag Attribute |
 |
JSP Custom Tag Library |
 |
Xml Bean |
Objects - Apache Struts
| Icon | MetaModel name |
|---|---|
 |
Struts Action / Common Struts Action |
 |
Struts Action Mapping |
 |
Struts Configuration File |
 |
Struts2 Configuration File |
 |
Struts Form Bean |
 |
Struts Forward |
 |
Struts Interceptor |
 |
Struts Interceptor Stack |
 |
Struts Package |
 |
Struts Result |
 |
Struts Validator |
 |
Validation |
 |
Validation Form Field |
 |
Validation Forms Set |
Objects - STXX (Presentation)
| Icon | MetaModel name |
|---|---|
 |
STXX Pipeline |
 |
STXX Transform |
 |
STXX Transforms File |
Objects - JPA (Persistence)
| Icon | MetaModel name |
|---|---|
 |
JPA Embeddable |
 |
JPA Embeddable Property |
 |
JPA Entity |
 |
JPA Entity Property |
 |
JPA Named Native Query |
 |
JPA Named Query |
 |
JPA ORM Configuration File |
 |
JPA Persistence Configuration File |
 |
JPA Persistence Unit |
 |
JPA SQL Result Set |
Objects - EJB (Persistence)
| Icon | MetaModel name |
|---|---|
 |
Entity Java Bean |
 |
Message Driven Java Bean |
 |
Session Java Bean |
Objects - Other (Spring related)
| Icon | MetaModel name |
|---|---|
 |
Singleton Java Bean |
 |
Spring Bean |
 |
Spring Beans File |
 |
Spring Controller |
 |
Spring View |
 |
CDI Named Bean |
 |
Spring Batch Job |
 |
Spring Batch Step |
Links - References detected by the analyzer when carrying out a pure Java analysis
| Link type | When is this type of link created? | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MENTION | This link is traced on following expressions (Callee always refers to a class or interface): "instance of" operator cast expression class literal this literal class creation array creation |
- if (b instanceof A . class) ... - A . this = 1; - B b = (B) new A(1); - B b [] = new A[5]; |
|
| THROW, RAISE, CATCH | These links are used to describe exception handling (Callee always refers to a class): Throw link is traced on "throws" clause of method declaration towards exceptions possibly raised by the method. Raise link is traced on "throw" statement towards type of the exception actually thrown by the method. Catch link is traced on "try" statement towards type of the exception parameter declared in catch clause(s). |
- void f () throws C1 {...} - throw new Exception() - try {...} catch (Throwable e) {...) |
|
| RELY ON | This link is used to describe typing. Caller uses callee to define its Java type. Callee always refers to a class or interface. | - void f (A a) {...} - A a [] = null; |
|
| ACCESS | This link is used to describe run-time interactions. It may be enriched by the following sub-types: Read Write Exec Member Array |
- return x - (read) - x = 1 - (write) - x++ - (read and write) - x[1] = 2 - (array not read) - x[] = {1,2} - (read) - f(1) - (exec) - x.toString() - (member) - x.f() - (member on x ; exec on f) - x.y = 1 - (member on x ;write on y) |
|
| INHERIT | This link is used to describe object hierarchy. It may be enriched by the following sub-types (Caller and callee always refer to classes or interfaces): Extend: class to super-class interface to super-interface Implement: class to super-interface(s) By extension the Inherit link is also used to describe method overriding as directly related to inheritance. In this case exclusive sub-types are available (Caller and callee always refer to methods): Hide: for static methods; Override: for instance methods; in addition link can be enriched by the Implement sub-type if overriding is from a non abstract overriding method to an abstract overridden one. |
- class C1 extends C2 implements I {...} - interface I1 extends implements I2 {...} |
|
| USE | This type is reserved for dynamic link resolution. It covers server side objects referencing: Select Insert Update Delete |
- | |
| PROTOTYPE | This link is reserved for J2EE components' support and is used as follows (Caller and callee always refer to a component and to a class or interface): Applet: between the applet component and its applet class. |
- | |
Links - References that are detected by the analyzer while analyzing JSP pages and Tag Files as client files
| Link Type | Situation | When is this type of link created? |
| USE | TypLib |
<!-- METADATA TYPE = "TypeLib" FILE = "TypLibFileName"--> |
| USE | Applet |
<APPLET CODE = "AppletCode" CODEBASE = "AppletCodeBase"> |
| USE | ActiveX through a variable |
x = new ActiveXObject("A.B") function f() { x.Method() Use link between f and A.B |
| USE | Dynamic data source | Use link between id_a and id_obj |
USE |
Database object
|
|
| USE | MAP | |
| MENTION | Indicates the area in which the ActiveX is mentioned | Mention link between f and A.B |
| MENTION | Indicates the area in which the class name is mentioned | Mention link between f and g |
| INCLUDE | Indicates the inclusion of a file | |
| CALL | Indicates a call to a file | |
| CALL | Indicates a function call | Call link between g and f |
| ACCESS | Indicates a access type link enters a property of an HTC component together with the associated PUT or GET function. | ACCESS link between xmlData and the getxmlData and putxmlData functions. |
| ACCESS and READ |
Read only access to a file | |
| ACCESS and READ |
Read only access to a variable | Read only access between f and x |
| ACCESS and WRITE |
Read and write access to a variable | Read and write access between f and y |
| ACCESS and PAGE_FORWARD | Indicates a redirection. Only available for analyzed IIS applications. | - |
| REFER | Indicates that a variable refers to another variable | Refer link between Application("y") and x |
| RELY ON and INSTANCE OF | Indicates that a variable is an instance of a class | INSTANCE_OF link between x and A.B |
| GO THROUGH | Indicates the error file(s) used. Only available for analyzed IIS applications. | - |
Links - References that are detected by the analyzer while analyzing the JSP page implementation class and/or Tag Handlers are dynamic references
For the dynamic references which are issued from a grep or have the caller located in a JSP script element as a declaration, expression or scriplet, a static link will be created. This new link has almost the same properties as the dynamic link, however the caller can be different. For example, when an object is located in an included file we will have a dynamic reference from the _jspService function of the JSP Page (resp. doTag method of a Tag File) and the object and a static reference from the included JSP File (resp. Tag File) and the object. Note that the main function of the generated servlet/handler class is a pure dynamic object. So, it cannot have static references and we will create them at the function’s parent (JSP Page/Tag File) level.
The following table summarizes the process of creation of the static links using the dynamic links while parsing generated servlet classes (‘Dynamic Caller’ are replace by ‘Static caller’):
| Caller: Dynamic Object | Link code located in | Caller: Static Object |
|---|---|---|
| _jspService | JSP page | JSP page |
| _jspService | JSP page | JSP page |
| servlet class | JSP page | JSP page |
| servlet class | JSP File (included file) | JSP File (included file) |
| caller | JSP Page or JSP File (included file) | JSP Page or JSP File (included file) |
Example:
fileA.jsp
<%! String redirectA; %>
<% redirectA = "/jsp/fileA.jsp"; %>
fileA.jsp/ includedA.jsp
<%@ include file="included.jsp"%>
<%! String includedA; %>
<% includedA = "/jsp/fileA.jsp"; %>
Links - EJB
The following lists describes references that are detected by the JEE analyzer and the context in which corresponding links are traced.Links between bean and class/interfaces are flagged as “Prototype” and are oriented as follows:
- From bean local and remote interfaces to the EJB itself,
- From the EJB itself to its bean class and, for entity bean, primary key class.
In addition the following links are also traced:
| Link Type | When is this type of link created? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIRE | 1. Traced between bean class member methods that are implicitly called by the EJB Container:
2. Traced between bean class/home interface and server side objects. For example in this standard ejb-jar.xml file: The signature of the method is created from the values of the tags <method-name> and <method-param>. The method is searched for using the home interfaces (for the findXXX) and the bean class (for the "select methods"). The abstract schema name identified by grep in the query "EJB-QL" is used to find the associated bean (the query can reference the abstract schema name of another bean). From the bean it is possible to retrieve the associated table names and then link resolution is possible. 3. Also traced between SEI.Mi (Service Endpoint Interface) and BC.Mi (Bean Class). Mi stands for methods that have the same signature in the SEI and the BC. The EJB must be a stateless session bean:
4. In addition, this link type is used for implicit invocations. They are used to reflect:
Caller always refers to a component or a class member method. Callee always refers to a class member method.
Note: "Fire" links are never escalated.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| USE SELECT, DELETE, UPDATE, INSERT | Traced between bean and server objects (tables). Bean --Usdui--> Table (U for Use, s for Select, d for Delete, u for Update, i for Insert)
The link Bean --Usdui--> Table is traced only with container managed persistence (cmp) beans. For Bean managed persistence (bmp) beans, this link is indirect and is represented by two links:
For example in this standard ejb-jar.xml file: The bean in question is found in the ejb-jar.xml file using its name. Persistence information is identified using descriptors specific to each server type: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PROTOTYPE |
This link type is reserved for J2EE components' support and is used as
follows:
For example the Webservices.xml (must be placed in the module directory) JAX-RPC mapping file (mapping.xml in the example) indicates that the mapping information between the web service operation and the java methods can be found in mapping.xml.
Note: "Prototype" links are never escalated.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACCESS |
These links correspond to inter-bean references. These references are
made via a logical name (declared in the ejb-jar.xml file and that
specifies the target ejb) used in the bean client code. The tags
containing this logical name are <ejb-ref> or
<ejb-local-ref>.
For example in this standard ejb-jar.xml file: Each bean specifies the list of other beans it accesses as well as the references used to do so. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| JOIN |
Traced between entity beans based on the abstract schema defined in
deployment descriptor (beneath the
<relationships>...</relationships> tag).
An entity bean (source EJB) is linked to another entity bean (destination EJB) only if navigation is possible from source EJB to destination EJB, i.e the relation-role in which source EJB is involved contains at least one cmr (container managed relationship) field allowing access to the destination EJB. Considering the example above, the source EJB TeamEJB will be linked to the destination EJB PlayerEJB because the cmr field players makes navigation possible from source to destination EJB. For the same reasons, PlayerEJB (now source EJB) will have Refer link to TeamEJB (destination EJB for this link). For each Join link, the information below is retrieved from the deployment descriptor and accessible in HTML Report:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Structural rules
The following rules are provided in the extension:
See also the following rules provided in the default CAST Assessment Model shipped with CAST Imaging Core:
| Technology | URL |
|---|---|
| JEE | https://technologies.castsoftware.com/rules?sec=t_140029&ref=|| |
The following extensions also provide JEE specific rules: