Vue.js - 1.2
Extension ID
com.castsoftware.vuejs
What’s new?
Please see Vue.js - 1.2 - Release Notes for more information.
Description
This extension provides support for Vue.js. Vue.js is an open-source JavaScript framework used to build user interface for web application: vuejs.org
In what situation should you install this extension?
If your Web application contains Vue.js source code used inside JavaScript files and you want to view these object types and their links with other objects, then you should install this extension.
This extension does note analyse any Vue.js source code within TypeScript files.
Supported Vue.js versions
| Version | Support |
|---|---|
| v2.x |
Supported template definitions
Vue.js has different methods to define a component’s template - these methods are shown here: https://vuejsdevelopers.com/2017/03/24/vue-js-component-templates/. The following table shows the methods that are currently supported by Vue.js extension:
| Pattern | Support |
|---|---|
| String | |
| Template literal | |
| X-Templates | |
| Inline | |
| Render functions | |
| JSX | |
| Single page components |
Unsupported template definition methods will not create links to any called functions.
AIP Core compatibility
This extension is compatible with:
| AIP Core release | Supported |
|---|---|
| 8.3.x |
Dependencies with other extensions
Some CAST extensions require the presence of other CAST extensions in
order to function correctly.
The Vue.js extension requires that the following other CAST
extensions are also installed:
- HTML5/JavaScript
- Web services linker service (internal technical extension)
What results can you expect?
Once the analysis has completed, you can view the results in the normal manner:
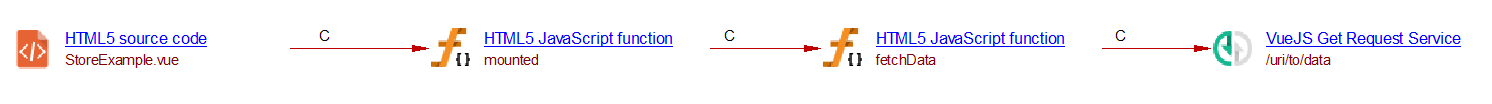
Objects
The following specific objects are displayed:
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
|
Vue.js Get Request Service |
|
Vue.js Post Request Service |
|
Vue.js Put Request Service |
|
Vue.js Delete Request Service |
Specific support
Store
The “Vuex.Store()” calls are searched for throughout the application, and the first parameter is used to resolve different links.
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
pageTitle: 'Home',
menu: menu,
user: {},
token: null,
message: {
type: null,
body: null
},
config: config
},
mutations: {
setAuth (state, { user, token }) {
state.user = user
state.token = token
global.helper.ls.set('user', user)
global.helper.ls.set('token', token)
},
setMenu (state, data) {
state.menu = data
},
setPageTitle (state, data) {
state.pageTitle = data
},
showMessage (state, type, body) {
state.message = { type, body }
}
},
actions: {
checkAuth ({ commit }) {
let data = {
user: global.helper.ls.get('user'),
token: global.helper.ls.get('token')
}
commit('setAuth', data)
},
checkPageTitle ({commit, state}, path) {
for (let k in state.menu) {
if (state.menu[k].href === path) {
commit('setPageTitle', state.menu[k].title)
break
}
}
}
}
})
export default store
the “sync()” calls are also used:
import store from './store'
import router from './router'
sync(store, router)
Dispatch
This extension supports “Vuex store dispatch” methods which are used to call shared functions. Here is an example of a classic architecture using this method:
In actions.type.js
export const FETCH_DATA = "fetchData";
In data.module.js
import { FETCH_DATA } from "./actions.type";
import Vue from "vue";
import axios from "axios";
import VueAxios from "vue-axios";
Vue.use(VueAxios, axios);
const actions = {
[FETCH_DATA]() {
return return Vue.axios.get('uri/to/data')
},
};
export default {
actions
};
In index.js
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
import data from "./data.module";
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
data
}
});
In StoreExample.vue
<template>
<div></div>
</template>
<script>
import { FETCH_DATA } from "@/store/actions.type";
export default {
name: "StoreExample",
mounted: function() {
this.$store.dispatch(FETCH_DATA)
}
};
</script>
This code gives the following results:
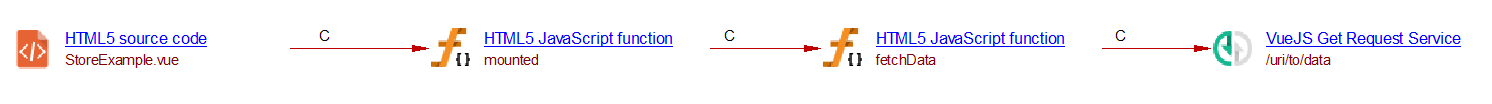
Webservices
Axios
The Vue.js extension supports webservices using Axios:
async onLogout() {
await this.$axios.$post('/api/oauth/logout');
this.setLogout(true);
this.setCurrentUser(null);
try {
await this.$axios.$get('/api/oauth/me')
} catch (e) {
// middleware redirects to login page
}
}
Giving the following result:
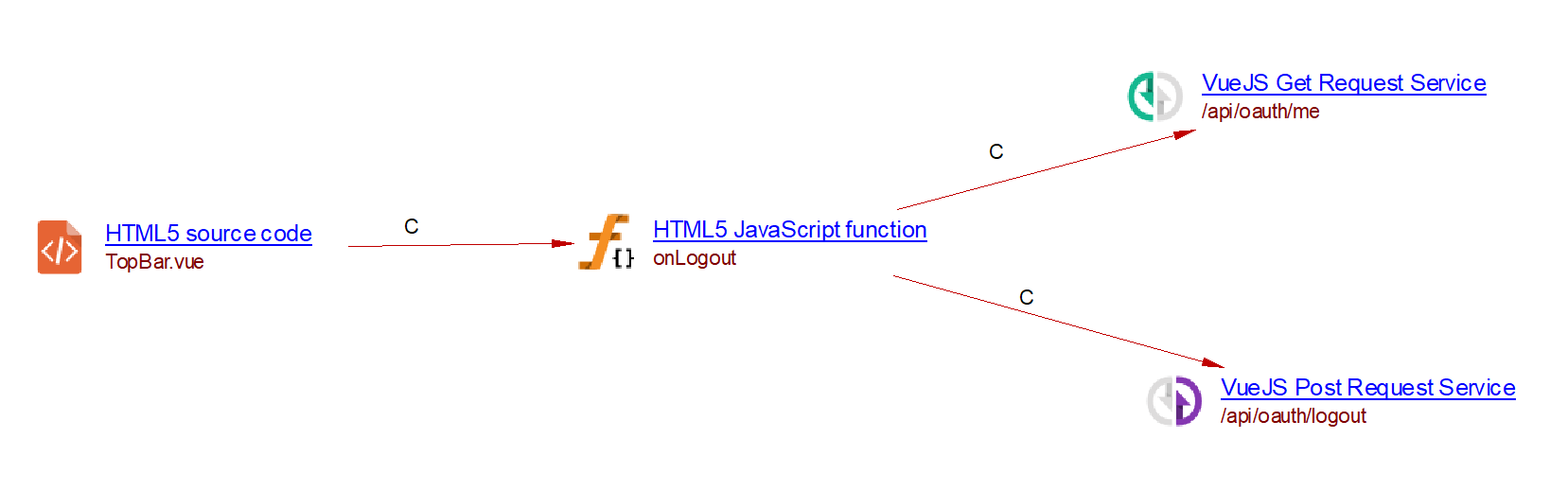
Vue-resources
The Vue.js extension supports webservices using vue-resources.
async onLogout() {
await this.$http.post('/api/oauth/logout');
this.setLogout(true);
this.setCurrentUser(null);
try {
await this.$http.$get('/api/oauth/me')
} catch (e) {
// middleware redirects to login page
}
}
Giving the following result:

Fetch
The Vue.js extension supports webservices using fetch:
async onLogout() {
await fetch('/api/oauth/logout');
this.setLogout(true);
this.setCurrentUser(null);
try {
await fetch('/api/oauth/me')
} catch (e) {
// middleware redirects to login page
}
}
Giving the following result:

Quality rules
The following structural rules are provided:
Known limitations
Functions passed as properties
In Vue.js, components can have properties, which could be functions. Links to those functions are currently unsupported.



