REST Service Calls for Java - 1.0
Extension ID
com.castsoftware.java.service
What’s new?
See Release Notes.
Description
This extension provides support for some web services calls from Java.
Supported REST client libraries
| Type | API |
|---|---|
| Native | java.net.URLConnection java.net.HttpURLConnection |
| JAX-RS | javax.ws.rs.client.SyncInvoker javax.ws.rs.client.AsyncInvoker javax.ws.rs.client.ClientBuilder javax.ws.rs.client.Client javax.ws.rs.client.WebTarget javax.ws.rs.client.Invocation javax.ws.rs.client.Invocation.Builder javax.ws.rs.core.UriBuilder jakarta.ws.rs.client.SyncInvoker jakarta.ws.rs.client.AsyncInvoker jakarta.ws.rs.client.ClientBuilder jakarta.ws.rs.client.Client jakarta.ws.rs.client.WebTarget jakarta.ws.rs.client.Invocation jakarta.ws.rs.client.Invocation.Builder org.jboss.resteasy.client.jaxrs.ResteasyClient org.jboss.resteasy.client.jaxrs.ResteasyWebTarget org.jboss.resteasy.client.ClientRequest com.sun.jersey.api.client.Client com.sun.jersey.api.client.WebResource org.glassfish.jersey.client.JerseyClient |
| Spring | org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder org.springframework.web.util.UriComponents org.springframework.web.util.HtmlUtils org.springframework.social.support.URIBuilder org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient |
| Apache | org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient org.apache.cxf.jaxrs.client.WebClient org.apache.http.client.HttpClient org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient org.apache.http.impl.nio.client.CloseableHttpAsyncClient org.apache.http.client.utils.URIBuilder org.apache.wink.client.Resource org.apache.wink.client.RestClient |
| Vert.x | io.vertx.core.http.HttpClientRequest io.vertx.ext.web.client.HttpRequest io.vertx.ext.web.client.WebClient |
| okhttp | com.squareup.okhttp.OkHttpClient okhttp3.OkHttpClient |
| Other | org.resthub.web.Client org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.FeignClient feign.Feign feign.RequestLine retrofit2.http.DELETE retrofit2.http.GET retrofit2.http.PATCH retrofit2.http.POST retrofit2.http.PUT |
Function Point, Quality and Sizing support
- Function Points (transactions): a green tick indicates that OMG Function Point counting and Transaction Risk Index are supported
- Quality and Sizing: a green tick indicates that CAST can measure size and that a minimum set of Quality Rules exist
| Function Points (transactions) | Quality and Sizing |
|---|---|
| ✅ | ❌ |
Compatibility
| Release | Operating System | Supported |
|---|---|---|
| v3/8.4.x | Microsoft Windows / Linux | ✅ |
| v2/8.3.x | Microsoft Windows | ✅ |
Dependencies with other extensions
The REST Service Calls for Java extension requires that ≥ 1.2.8-funcrel of the JEE Analyzer is also installed and used in order to ensure the most complete set of results. This dependency with the JEE Analyzer is not automatically handled when downloading the REST Service Calls for Java extension via CAST Extension Downloader, CAST Server Manager or AIP Console, therefore you must MANUALLY download and install the JEE Analyzer before starting an analysis.
What results can you expect?
Features
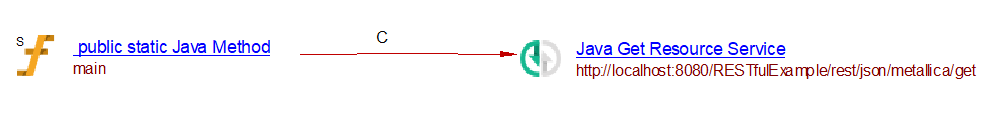
This extension analyzes web service calls made from Java code through classic fluent APIs. For example with com.sun.jersey:
import com.sun.jersey.api.client.Client;
import com.sun.jersey.api.client.ClientResponse;
import com.sun.jersey.api.client.WebResource;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Client client = Client.create();
WebResource webResource = client
.resource("http://localhost:8080/RESTfulExample/rest/json/metallica/get");
ClientResponse response = webResource.accept("application/json")
.get(ClientResponse.class);
}
}
Client side load balancing
Usage of org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerClient allows to choose a service to call so impacts the URL called:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import java.net.URI;
class Main
{
@Autowired
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient;
void f()
{
RestTemplate client ;
ServiceInstance serviceInstance = loadBalancerClient.choose("user-auth");
String path = serviceInstance.getUri().toString() + "/oauth/token";
client.put(path, client);
}
}

Feign
Feign is a declarative web service client which makes writing web service clients easier. Native sample: “RequestLine” annotation indicates the presence of feign web service:
interface GitHub {
@RequestLine("GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")
List<Contributor> contributors(@Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repo);
}
public static class Contributor {
String login;
int contributions;
}
public class MyApp {
public static void main(String... args) {
GitHub github = Feign.builder()
.decoder(new GsonDecoder())
.target(GitHub.class, "https://api.github.com");
// Fetch and print a list of the contributors to this library.
List<Contributor> contributors = github.contributors("OpenFeign", "feign");
for (Contributor contributor : contributors) {
System.out.println(contributor.login + " (" + contributor.contributions + ")");
}
}
}

“FeignClient” annotation associated with “RequestMapping” and “GetMapping” annotations indicates the presence of feign web service:
import java.util.List;
@FeignClient(
name = "${client.name}",
path= "${client.path}",
configuration = FeignConfiguration.class
)
public interface ClientConfiguration {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, value = "/services/clients")
List<SupplierTransitionDTO> getData(@RequestBody List<String> codes) throws FeignException;
}

@FeignClient(name = "Client", url = "${build.api.url}", path = "/api/v1")
public interface ClientConfiguration {
@GetMapping("/sites/{site-id}/clients")
ConsentResponse getConfiguration(
@PathVariable("site-id") String siteId,
@RequestParam("types") List<ConfigType> types);
}

Retrofit2.http
With Retrofit 2, endpoints are defined inside an interface using special retrofit annotations to encode details about the parameters and request method. Annotations like “GET”, “POST”, “PUT”, “DELETE” and “PATCH”, for example:
import retrofit2.http.GET;
public interface ExampleGetService {
@GET("getservice.example")
Single<ExampleApi> getMode();
}

Objects
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Delete Resource Service |
 |
Get Resource Service |
 |
Post Resource Service |
 |
Put Resource Service |
 |
Patch Resource Service |
Rules
None.
Limitations
- When the code uses a custom URL builder, we cannot evaluate the URL.
- When the standard java API is encapsulated in a custom method where the “http method” (put, get, post, delete) is passed as a parameter, the dynamic evaluation will generally fail.
class MyHttpCall
{
void execute(String url, String method)
{
Client client = ClientBuilder.newClient();
WebTarget myResource = client.target(url);
if (method == "GET")
{
String response = myResource.request(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN).get(String.class);
}
else if (method == "PUT")
{
myResource.request(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN).put(null);
}
}
}
- Manual creation of feign clients is not supported