Reactive Programming for Java - 1.0
Extension ID
com.castsoftware.java.reactive
What’s new?
See Reactive Programming for Java - 1.0 - Release Notes.
Description
This extension provides support for Java Reactive web operation calls made from Java code through packet org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server
The chosen approach for modelization is about web operation object on the server-side which is shown in more detail in the following table.
Supported API
| Method | Support | Parameter(s) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.route |
|
Normally used to pair with RouterFunctions.Builder.X methods |
|
RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
Quick explanation:
|
||
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.nest |
RequestPredicate RouterFunction |
Quick explanation: 1 web operation object:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.route |
RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
Quick explanation: 1 web operation object:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.add |
RouterFunction |
Quick explanation: 2 web operation objects: First:
Second:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.nest |
RequestPredicate Supplier> |
Quick explanation: 2 web operation objects: First:
Second:
|
|
RequestPredicate Consumer |
|||
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.path |
RequestPredicate Supplier> |
Quick explanation: 1 web operation object:
|
|
RequestPredicate Consumer |
|||
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.GET |
HandlerFunction |
// |
|
String HandlerFunction |
Quick explanation: 3 web operation objects: First:
Second:
Third:
|
||
RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
// |
||
String RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
Quick explanation: 2 web operation objects: First:
Second:
Normal url /posts is no longer valid based on real test. |
||
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.POST |
HandlerFunction |
// |
|
String HandlerFunction |
// |
||
RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
// |
||
String RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
// |
||
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.PUT |
HandlerFunction |
// |
|
String HandlerFunction |
// |
||
RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
// |
||
String RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
// |
||
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.DELETE |
HandlerFunction |
// |
|
String HandlerFunction |
// |
||
RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
// |
||
String RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
// |
||
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.HEAD |
HandlerFunction |
// |
|
String HandlerFunction |
// |
||
RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
// |
||
String RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
// |
||
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.before |
Function | Quick explanation: 3 web operation objects: First:
Second:
Third:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.after |
BiFunction | ||
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions.Builder.filter |
HandlerFilterFunction | Quick explanation: 1 web operation object:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunction.andRoute |
RequestPredicate HandlerFunction |
Quick explanation: 2 web operation objects: First:
Second:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunction.andNest |
RequestPredicate RouterFunction |
Quick explanation: 2 web operation objects: First:
Second:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunction.andOther |
RouterFunction |
Quick explanation: 3 web operation objects: First:
Second:
Third:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunction.and |
RouterFunction |
Quick explanation: 3 web operation objects: First:
Second:
Third:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.GET |
String |
// |
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.POST |
String |
// |
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.PUT |
String |
// |
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.DELETE |
String |
// |
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.HEAD |
String |
// |
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.all |
|
Quick explanation: 1 web operation object:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.path |
String |
// |
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.method |
HttpMethod |
Quick explanation: 1 web operation object:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.methods |
HttpMethod... |
Quick explanation: 3 web operation objects: First:
Second:
Third:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicate.and |
RequestPredicate |
Quick explanation: 1 web operation object:
|
|
org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicate.or |
RequestPredicate |
Quick explanation: 2 web operation objects: First:
Second:
|
Supported handler binding
Lambda
Lambda to internal MethodCall
route(GET("/posts"), A->A.B())
Handler is passed as a lambda A->A.B() pointing to an internal MethodCall A.B() which creates a routing value of GET request and URL value of /posts
Both A (class) and B (method) are declared and defined by user.
Lambda to external MethodCall
route().path("/posts", builder -> builder.GET(ClassC::D)).build()
Handler is passed as MethodReference ClassC::D inside an external MethodCall builder.GET() which creates a routing value of GET request and URL value of /posts/{}
GET is an API method found in instance of builder of an dedicated API class
Both ClassC (class) and D (method) are declared and defined by user
MethodCall
route(GET("/posts"), E())
Handler is passed as a call of an internal method E() which creates a routing value of GET request and URL value of /posts
MethodReference
route(GET("/posts"), this::all)
Handler is passed as a reference to an internal method all which creates a routing value of GET request and URL value of /posts
Identifier
route(GET("/posts"), all)
Handler is passed as a variable - an identifier all used to referencing a method which creates a routing value of GET request and URL value of /posts
The referenced method is determined based following this order:
@Bean method specified by @Qualifier >> @Bean method annotated with @Primary >> @Bean method with matching declared Bean name >> @Bean method with matching normal name >> Unique @Bean method found (regardless of name).
@Bean method specified by @Qualifier
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> A (@Qualifier("C") HandlerFunction<ServerResponse> B) {
return route(GET("/posts/{id}"), B);
}
C is the name declared by the @Bean that annotates the method or the name of the method itself.
@Bean method annotated with @Primary
@Primary
@Bean()
public HandlerFunction<ServerResponse> D() {
return E;
}
@Bean method with declared Bean name
@Bean("F")
public HandlerFunction<ServerResponse> G() {
return G;
}
F is the Bean name of method with G as its normal name, in this case the name F takes precedence over the name G.
Unique @Bean method found
@Bean("B")
public HandlerFunction<ServerResponse> Y() {
return Z;
}
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> newRoute(HandlerFunction<ServerResponse> X) {
return route(GET("/posts/{id}"), X);
}
newRoute will automatically bind Y to its argument X, in other word X will be replaced with Y since Y is the only present @Bean method in the current configuration.
Multiple handlers
RouterFunctions.route()
.GET("/hello", A)
.filter(B)
.build()
One web operation object is created with 2 binding handlers: A and B
Compatibility
| AIP Core release | Supported |
|---|---|
| 8.3.x | |
| com.castsoftware.jee.1.3.5-funcrel | |
| com.castsoftware.internal.platform.0.9.15 | |
| com.castsoftware.wbslinker.1.7.23-funcrel |
Dependencies with other extensions
The Reactive Programming for Java extension requires that ≥ 1.3.5-funcrel of the JEE Analyzer is also installed and used in order to ensure the most complete set of results. This dependency with the JEE Analyzer is not automatically handled when installing the Reactive Programming for Java extension, therefore you must ensure that the JEE Analyzer is already installed before starting an analysis.
Download and installation instructions
The extension will not be automatically installed by CAST Console, therefore you should ensure that the extension is manually installed using the Application - Extensions interface:
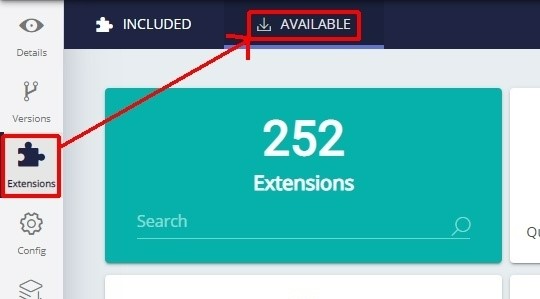
What results can you expect?
Objects
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
|
Spring WebFlux Get Operation |
|
Spring WebFlux Put Operation |
|
Spring WebFlux Post Operation |
|
Spring WebFlux Delete Operation |
|
Spring WebFlux Any Operation |
Examples
Spring 5 examples
Axon lock application
From axon-lock\axon-app\src\main\java\daggerok\AxonApplication.java
@Bean RouterFunction<ServerResponse> routes() {
return
route(POST("/api/v1/register-guest"), request -> {
final String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
final URI uri = request.uriBuilder()
.path(uuid)
.build();
return created(uri).body(request.bodyToMono(Map.class)
.map(map -> map.get("name"))
.map(name -> {
log.info("create user {}", name);
return "";
}).subscribeOn(Schedulers.elastic()), String.class);
})
;
}
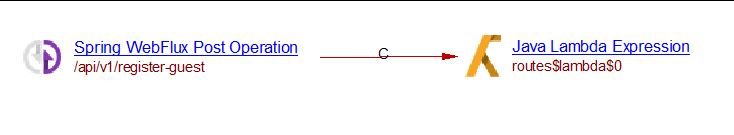
One Java Reactive POST object:
POST("/api/v1/register-guest")
And its associated handler:
request -> {
final String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
final URI uri = request.uriBuilder()
.path(uuid)
.build();
return created(uri).body(request.bodyToMono(Map.class)
.map(map -> map.get("name"))
.map(name -> {
log.info("create user {}", name);
return "";
}).subscribeOn(Schedulers.elastic()), String.class);
}
Result:
Spring data count query
From spring-data-jpa-count-query-fix\src\main\java\daggerok\App.java
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
class WebfluxRoutesConfig {
private final OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Bean
HandlerFunction<ServerResponse> getCountQueryHandler() {
return request ->
ok().contentType(APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.body(Flux.fromIterable(orderRepository.findAllPrices()), Price.class);
}
@Bean
HandlerFunction<ServerResponse> getOrdersHandler() {
return request ->
ok().contentType(APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.body(Flux.fromIterable(orderRepository.findAll()), Order.class);
}
@Bean
HandlerFunction<ServerResponse> fallbackHandler() {
return request -> {
final URL url = Try.of(() -> request.uri().toURL())
.getOrElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("=/"));
final String protocol = url.getProtocol();
final int defaultPort = "https".equals(protocol) ? 443 : 80;
final int currentPort = url.getPort();
final int port = currentPort == -1 ? defaultPort : currentPort;
final String baseUrl = format("%s://%s:%d", protocol, url.getHost(), port);
return ok().body(Flux.just(
format("GET orders -> %s/api/orders/", baseUrl),
format("GET pages -> %s/api/", baseUrl),
format("GET -> %s/", baseUrl)
), String.class);
};
}
@Bean
RouterFunction routes(final HandlerFunction<ServerResponse> fallbackHandler) {
return
nest(
path("/"),
nest(
accept(APPLICATION_JSON),
route(
GET("/api/orders"),
getOrdersHandler()
)
).andNest(
accept(APPLICATION_JSON),
route(
GET("/api"),
getCountQueryHandler()
)
)
).andOther(
route(
GET("/home"),
fallbackHandler
)
)
;
}
}
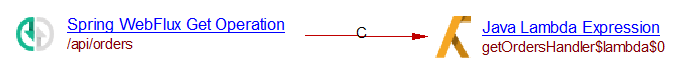
Three Java Reactive objects:
First GET object:
path("/") ... GET("/api/orders")
And its corresponding handler:
request ->
ok().contentType(APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.body(Flux.fromIterable(orderRepository.findAll()), Order.class)
Result:
Second GET object:
path("/") ... GET("/api")
And its corresponding handler:
request ->
ok().contentType(APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.body(Flux.fromIterable(orderRepository.findAll()), Order.class)
Result:

Third GET object:
GET("/home")
And its corresponding handler:
fallbackHandler
Result:

About Project Reactor
Although it is primarily a library for reactive programming and focusing on handling asynchronous data streams using reactive types like Mono and Flux, it does not inherently provide routing or HTTP method creation functionalities.
It can be used within the context of an HTTP server framework to handle incoming requests reactively and execute corresponding logic based on the requested URL paths and HTTP methods.
Limitation
Not enough use of functional programming pattern in client applications to validate the current support performance.




