AWS Java - 1.2
Extension ID
com.castsoftware.awsjava
What’s new?
See Release Notes.
Supported services and frameworks
| Services | Framework: SDK 1.x, 2.x |
|---|---|
| S3 | ✅ |
| Lambda creation and link to handler | ❌ |
| Lambda invoke | ✅ |
| SNS publish | ✅ |
| SNS subscription: http | ✅ |
| SNS subscription: email/SMS | ✅ |
| SNS subscription: sqs | ✅ |
| SNS subscription: lambda | ✅ |
Note that:
- the support of SQS services with SDK for java is provided by com.castsoftware.mqe .
- the support of AWS dynamodb services with SDK for Java is provided by com.castsoftware.nosqljava .
Function Point, Quality and Sizing support
- Function Points (transactions): a green tick indicates that OMG Function Point counting and Transaction Risk Index are supported
- Quality and Sizing: a green tick indicates that CAST can measure size and that a minimum set of Quality Rules exist
| Function Points (transactions) | Quality and Sizing |
|---|---|
| ✅ | ❌ |
Compatibility
| Release | Operating System | Supported |
|---|---|---|
| v3/8.4.x | Microsoft Windows / Linux | ✅ |
| v2/8.3.x | Microsoft Windows | ✅ |
What results can I expect?
Objects
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Java Call to AWS Lambda Function |
 |
Java Call to AWS unknown Lambda Function |
 |
Java AWS Simple Queue Service Receiver |
 |
Java AWS Simple Queue Service Publisher |
 |
Java AWS Unknown Simple Queue Service Receiver |
 |
Java AWS Unknown Simple Queue Service Publisher |
 |
Java AWS SNS Publisher |
 |
Java AWS SNS Subscriber |
 |
Java AWS SNS Unknown Publisher |
 |
Java AWS SNS Unknown Subscriber |
 |
Java AWS SMS, Java AWS Email |
 |
Java AWS Post Resource Service |
 |
Java AWS S3 Bucket |
 |
Java AWS unknown S3 Bucket |
Supported elements
Support for Lambda functions
- Lambda services allow executing some source code on the cloud. The execution can be set to be triggered by some AWS events.
- Lambda functions can be deployed using several deployment frameworks. The supported deployment frameworks are listed on AWS Lambda.
- When a lambda function is created and its runtime is java, the current extension is responsible for linking the lambda objects and their triggers with the java handler functions.
Example
Let us consider a source code defining a lambda function having a java runtime (for instance java8) and the handler function is given by the handler function fullname. If the lambda function is deployed using a supported deployment framework (such as CloudFormation), the analysis will create a lambda function. If the current extension finds a java method matching the handler fullname a link to that java method will be added from the lambda function.

Some applications are using a monolithic pattern: only one handler function is used for many (if not all) API Gateways. That handler function then dispatches the call to sub-handler functions using switches based on the URLs. Ideally, in the modelization, each API Gateway should be linked to its dedicated sub-handler function. However, in our modelization, all API Gateways will be linked to the root handler function.
Support for S3
Supported S3 APIs for SDK v1
For the following methods of the com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3 client we create links to the bucket:
| Link Type | Methods |
|---|---|
| useUpdateLink | putObject, uploadPart |
| useInsertLink | putObject, uploadPart |
| useSelectLink | getObject, listObjects, listObjectsV2, getObjectAsString, listObjects, listObjectsV2 |
| useDeleteLink | deleteBucket, deleteObject, deleteObjects |
| callLink | changeObjectStorageClass deleteBucketAnalyticsConfiguration deleteBucketCrossOriginConfiguration deleteBucketEncryption deleteBucketIntelligentTieringConfiguration deleteBucketInventoryConfiguration deleteBucketLifecycleConfiguration deleteBucketMetricsConfiguration deleteBucketPolicy deleteBucketReplicationConfiguration deleteBucketTaggingConfiguration deleteBucketWebsiteConfiguration deleteObjectTagging deleteVersion disableRequesterPays doesBucketExist doesBucketExistV2 doesObjectExist download enableRequesterPays generatePresignedUrl getBucketAccelerateConfiguration getBucketAcl getBucketAnalyticsConfiguration getBucketCrossOriginConfiguration getBucketIntelligentTieringConfiguration getBucketInventoryConfiguration getBucketLifecycleConfiguration getBucketLocation getBucketLoggingConfiguration getBucketMetricsConfiguration getBucketNotificationConfiguration getBucketOwnershipControls getBucketPolicy getBucketReplicationConfiguration getBucketTaggingConfiguration getBucketVersioningConfiguration getBucketWebsiteConfiguration getObjectAcl AccessControlList getObjectMetadata getObjectTagging getUrl headBucket initiateMultipartUpload isRequesterPaysEnabled listParts listVersions restoreObject restoreObjectV2 setBucketAccelerateConfiguration setBucketAcl setBucketAnalyticsConfiguration setBucketCrossOriginConfiguration setBucketIntelligentTieringConfiguration setBucketInventoryConfiguration setBucketLifecycleConfiguration setBucketLoggingConfiguration setBucketMetricsConfiguration setBucketNotificationConfiguration setBucketOwnershipControls setBucketPolicy setBucketReplicationConfiguration setBucketTaggingConfiguration setBucketVersioningConfiguration setBucketWebsiteConfiguration setObjectAcl setObjectRedirectLocation setObjectTagging setEndpoint setRequestPaymentConfiguration shutdown createBucket |
Supported S3 APIs for SDK v2
For the following methods of the software.amazon.awssdk.services.s3.S3Client client we create links to the bucket:
| Link Type | Methods |
|---|---|
| useUpdateLink | putObject, uploadPart, restoreObject |
| useInsertLink | completeMultipartUpload, putObject |
| useSelectLink | getObject, getObjectAsBytes, listObjects, listObjectsV2, listObjectsV2Paginator |
| useDeleteLink | deleteBucket, deleteObject, deleteObjects |
| callLink | abortMultipartUpload createBucket createMultipartUpload deleteBucketAnalyticsConfiguration deleteBucketCors deleteBucketEncryption deleteBucketIntelligentTieringConfiguration deleteBucketInventoryConfiguration deleteBucketLifecycle deleteBucketMetricsConfiguration deleteBucketOwnershipControls deleteBucketPolicy deleteBucketReplication deleteBucketTagging deleteBucketWebsite deleteObjectTagging deletePublicAccessBlock getBucketAccelerateConfiguration getBucketAcl getBucketAnalyticsConfiguration getBucketCors getBucketEncryption getBucketIntelligentTieringConfiguration getBucketInventoryConfiguration getBucketLifecycleConfiguration getBucketLocation getBucketLogging getBucketMetricsConfiguration getBucketNotificationConfiguration getBucketOwnershipControls getBucketPolicy getBucketPolicyStatus getBucketReplication getBucketRequestPayment getBucketTagging getBucketVersioning getBucketWebsite getObjectAcl getObjectLegalHold getObjectLockConfiguration getObjectRetention getObjectTagging getObjectTorrent getObjectTorrentAsBytes getPublicAccessBlock headBucket headObject listBucketAnalyticsConfigurations listBucketIntelligentTieringConfigurations listBucketInventoryConfigurations listBucketMetricsConfigurations listMultipartUploads listMultipartUploadsPaginator listObjectVersions listObjectVersionsPaginator listParts listPartsPaginator putBucketAccelerateConfiguration |
Example
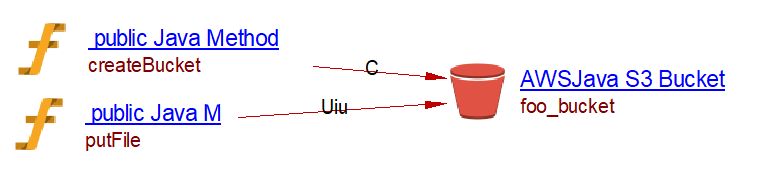
This code will create a S3 Bucket named “foo_bucket” on an AWS server in region “AP_SOUTH_1” and puts an object in it
package aws.example.s3;
import com.amazonaws.regions.Regions;
import com.amazonaws.regions.Region;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3ClientBuilder;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.model.Bucket;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
public class S3Manager {
public void createBucket() {
Region region = Region.getRegion(Regions.AP_SOUTH_1);
final AmazonS3 s3 = AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard().withRegion(region).build();
Bucket b = s3.createBucket("foo_bucket");
}
public void putFile(String file_path) {
Region region = Region.getRegion(Regions.AP_SOUTH_1);
final AmazonS3 s3 = AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard().withRegion(region).build();
String key_name = Paths.get(file_path).getFileName().toString();
s3.putObject("foo_bucket", key_name, new File(file_path));
}
}
Known limitations for S3
- createPresignedPost API is not supported. However the call to this method is represented by a callLink to the bucket similar to other API methods in S3Client.
Support for Lambda invocation
Only the invoke method of software.amazon.awssdk.services.lambda.LambdaClient (SDK V1) and com.amazonaws.services.lambda.AWSLambda (SDK V2) is currently supported.
Example
The analysis of the following source code will create a Java Call to AWS Lambda Function object named functionName with a callLink from the invokeFunction to that object:
import com.amazonaws.auth.profile.ProfileCredentialsProvider;
import com.amazonaws.regions.Regions;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.AWSLambda;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.AWSLambdaClientBuilder;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.model.InvokeRequest;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.model.InvokeResult;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.model.ServiceException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class FooClass {
public static void invokeFunction(LambdaClient awsLambda, String functionName) {
InvokeRequest invokeRequest = new InvokeRequest()
.withFunctionName("functionName")
.withPayload("{\n" +
" \"Hello \": \"Paris\",\n" +
" \"countryCode\": \"FR\"\n" +
"}");
InvokeResult invokeResult = null;
AWSLambda awsLambda = AWSLambdaClientBuilder.standard()
.withCredentials(new ProfileCredentialsProvider())
.withRegion(Regions.US_WEST_2).build();
invokeResult = awsLambda.invoke(invokeRequest);
}
}
@LambdaFunction annotation
The following two annotations (equally named) are supported (one for Android and the other one for Java applications):
- com.amazonaws.mobileconnectors.lambdainvoker.LambdaFunction
- com.amazonaws.services.lambda.invoke.LambdaFunction
The example below reproduced from the official documentation https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/with-android-example.html , illustrates how one can define (but not implement) the lambda function by annotating the AndroidBackendLambdaFunction method.
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/with-android-example.html
import com.amazonaws.mobileconnectors.lambdainvoker.LambdaFunction;
public interface MyInterface {
/
* Invoke the Lambda function "AndroidBackendLambdaFunction".
* The function name is the method name.
*/
@LambdaFunction
ResponseClass AndroidBackendLambdaFunction(RequestClass request);
}
The @LambdaFunction annotation maps the specific client method to the same-name Lambda function. The expected behavior of the JEE analyzer is to resolve the actual Lambda Function invocation via method calls (elsewhere) to the annotated interface methods. The com.castsoftware.awsjava extension on the other hand will create a Java Call to AWS Lambda Function object and the respective incoming callLink from the annotated interface method AndroidBackendLambdaFunction.
Support for SNS
The following APIs are supported:
For SDK V1:
- com.amazonaws.services.sns.AmazonSNS.publish
- com.amazonaws.services.sns.util.Topics.subscribeQueue
- com.amazonaws.services.sns.AmazonSNS.subscribe
For SDK V2
- software.amazon.awssdk.services.sns.SnsClient.publish
- software.amazon.awssdk.services.sns.SnsClient.subscribe
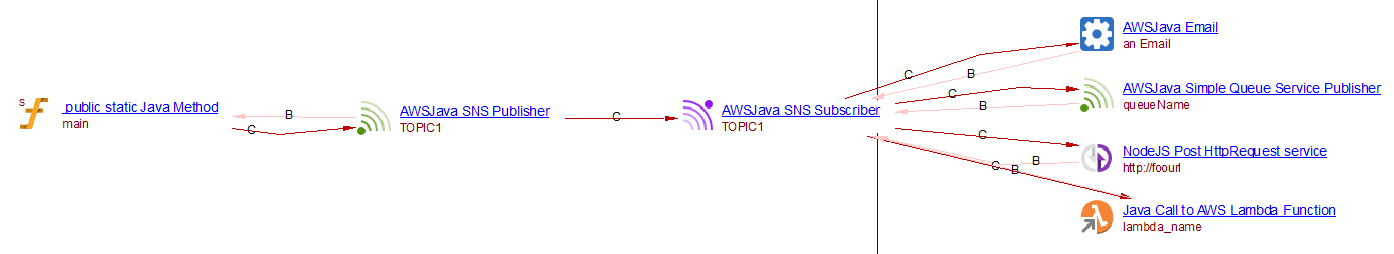
For the publish method a Java AWS SNS Publisher object is created. Its name is that of the topic. For the subscribe methods, a Java AWS SNS Subscriber object is created. Its name is that of the topic. Then for each supported protocol, an object is created with a callLink from the subscriber to that object. The supported protocols are the following:
| Protocol | Object created | Name of the object |
|---|---|---|
| Java AWS Email | an Email (the email addresses are not evaluated) | |
| sms | Java AWS SMS | an SMS (the SMS numbers are not evaluated) |
| http/https | Java AWS Post Service | the url (evaluated from the endpoint) |
| sqs | Java AWS Simple Queue Service Publisher | the name of the queue (evaluated from the endpoint) |
| lambda | Java Call to AWS Lambda Function | the name of the lambda function (evaluated from the endpoint) |
The com.castsoftware.wbslinker extension will create a callLink between the SNS Publishers and SNS Subscribers which have the same name.
Example
When analyzing the following source code:
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3ClientBuilder;
import com.amazonaws.services.sns.AmazonSNS;
import com.amazonaws.services.sns.AmazonSNSClientBuilder;
import com.amazonaws.services.sns.model.PublishRequest;
import com.amazonaws.services.sns.model.CreateTopicRequest;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3ClientBuilder;
import com.amazonaws.services.sns.model.SubscribeRequest;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String TOPIC_NAME = "extended-client-topic";
final Regions region = Regions.DEFAULT_REGION;
final AmazonSNS snsClient = AmazonSNSClientBuilder.standard().withRegion(region).build();
final String topicArn = snsClient.createTopic(
new CreateTopicRequest().withName("TOPIC1")
).getTopicArn();
snsClient.publish(topicArn, "message");
}
public static void subscribe(String[] args) {
final String TOPIC_NAME = "extended-client-topic";
final Regions region = Regions.DEFAULT_REGION;
final AmazonSNS snsClient = AmazonSNSClientBuilder.standard().withRegion(region).build();
final String topicArn1 = snsClient.createTopic(
new CreateTopicRequest().withName("TOPIC1")
).getTopicArn();
snsClient.subscribe(topicArn1, "email", "lili@lala.com");
snsClient.subscribe(new SubscribeRequest(topicArn1, "email", "lili@lala.com"));
snsClient.subscribe(new SubscribeRequest(topicArn1, "sqs", "arn:partition:service:region:account-id:queueName"));
snsClient.subscribe(new SubscribeRequest()
.setTopicArn(topicArn1)
.setProtocol("http")
.setEndpoint("http://foourl"));
snsClient.subscribe(new SubscribeRequest()
.withTopicArn(topicArn1)
.withProtocol("lambda")
.withEndpoint("fooarn:function:lambda_name:v2"));
}
}
Linking
The com.castsoftware.wbslinker extension is responsible for matching Java Call to AWS Lambda Function objects to Lambda Function objects such as Java AWS Lambda Function during application-level analysis.
Data sensitivity
This extension is capable of setting a property on AWS S3 Bucket objects for the following:
- custom sensitivity
- GDPR
- PCI-DSS
See Data Sensitivity for more information.
Known limitations
- No custom lambda function resolver is supported, i.e. that passed to lambdaFunctionNameResolver (connected to the building of LambdaInvokerFactory).
- Use of Consumer Builder for SDK is not supported.
- Monolithic pattern for lambda functions is not properly supported.