TypeScript support
Support of arrow functions and methods
Arrow functions which have been introduced in typescript following ES6 standard (also known as ES2015) are supported. Since arrow functions are equivalent to standard functions, the same function objects are created by the analyzer for both standard functions and arrow functions. Arrow functions can also define methods in which case method objects are created by the analyzer. Examples of arrow functions and methods are provided in the main section of this documentation.
Support of anonymous functions
For anonymous functions, the analyzer creates function objects named <Anonymous$i> where $i is incremented such that each anonymous function object has a unique fullname.
Support of Web Services
XMLHttpRequest
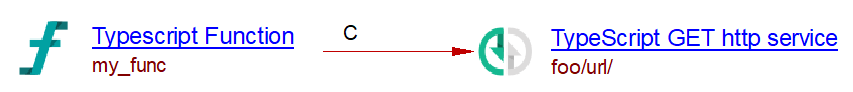
The analysis of the following code will create a TypeScript GET http service named “foo/url” and a callLink between my_func function and that service :
function my_func(){
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.open("GET", "foo/url", false);
xhttp.send();
}
fetch
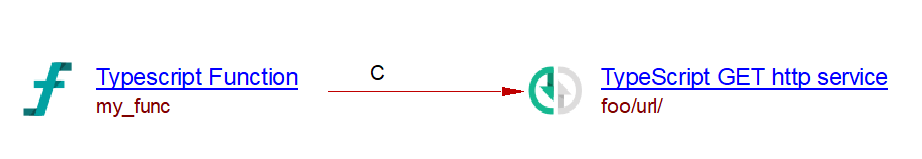
The analysis of the following code will create a TypeScript POST http service named “foo/url” and a callLink between my_func function and that service:
function my_func(){
const response = await fetch('foo/path', {
method: 'POST'
})
}

Window variable
The JavaScript window variable can be used to pass values such as urls. The windows variable is accessible from all modules. So when analyzing the following modules:
module1.py
window.myurl = "foo/url/"
module2.py
function my_func(){
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.open("GET", window['myurl'], false);
xhttp.send();
}
…a webservice object is created with the URL set through the window variable: