Cassandra for Java - 1.0
Extension ID
com.castsoftware.java.cassandra
What’s New?
Please see Cassandra for Java - 1.0 - Release Notes for more information.
In what situation should you install this extension?
This extension is specifically targeted at the Cassandra for Java framework and should be used in conjunction with the JEE Analyzer extension and the Cassandra extension. CRUD operations and Queries (@Query annotations) are supported, along with datastax queries. When client code uses any of these coding mechanisms, this extension, along with Cassandra extension, will create the links from the calling method to the Cassandra Java CQL Query and between the Cassandra Java CQL Query and the Cassandra Java Table/Cassandra CQL Table.
Note that there are two types of table because they may originate in .cql files, Cassandra CQL Table, or in java code, Cassandra Java Table. The Cassandra extension is responsible for creating the tables and the links. This helps form the complete transaction.
Supported releases
| Apache Cassandra | Supported |
|---|---|
| 4.x | |
| 3.x | |
| 2.x | |
| 1.x |
AIP Core compatibility
This extension is compatible with:
| AIP Core release | Supported |
|---|---|
| 8.3.x |
Dependencies with other extensions
Some CAST extensions require the presence of other CAST extensions in order to function correctly. The Cassandra for Java extension requires that the following other CAST extensions are also installed:
- CAST AIP Internal extension (internal technical extension)
- Cassandra extension
Note that when using the CAST Extension Downloader to download the extension and the Manage Extensions interface in CAST Server Manager to install the extension, any dependent extensions are automatically downloaded and installed for you. You do not need to do anything.
Download and installation instructions
You will need to manually install the extension using the Application - Extension interface in CAST Console.
What results can you expect?
Once the analysis/snapshot generation has completed, you can view the results in the normal manner. Some codeexamples are also shown below.
Objects
| Icon | Object Type |
|---|---|
|
Cassandra Java Operation |
|
Cassandra Java CQL Query |
|
Cassandra Java Schema |
|
Cassandra Java Table |
|
Cassandra Java Table Column |
|
Cassandra Java Index |
|
Cassandra Java Primary Key |
Database access with Spring Framework
Spring Data repository abstraction is focused on abstracting out the code required to implement the data access layers across different persistence mechanisms. CassandraRepository is used for data access layer. Using @Table annotation, the bean is directly mapped to a Cassandra data table. Also each property is defined as a type of primary key or a simple column.
Native queries (@Query Annotation)
When using @Query annotation, we create a Cassandra Java CQL Query object. The query Java code example:
DataTableRepository.java
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.repository.CassandraRepository;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.repository.Query;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface DataTableRepository
extends CassandraRepository<DataTable, DataTableKey>, DataTableRepositoryCustom {
@Query("SELECT * FROM data_table WHERE table_id = ?0 and year = ?1 order by ts DESC limit 1")
Optional<SensorIndex> findLatestTable(final String tableId, final Integer year);
}
The table Java class:
DataTable.java
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.mapping.Column;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.mapping.PrimaryKey;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.mapping.Table;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
@Value
@Builder(builderClassName = "Builder")
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE, force = true)
@Table("data_table")
public class DataTable {
@PrimaryKey
private final DataTableKey key;
@Column("value")
private final BigDecimal value;
}
The CQL file containing table creation code:
data_table.cql
CREATE TABLE data_table (
key text,
value text
PRIMARY KEY ((key), value));
The expected result:

CRUD method calls
The CRUD method calls supported with the Java Cassandra extension are enumerated in the table below:
Class |
Methods |
|---|---|
| org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository | count, delete, deleteAll, deleteById, existsById, findAll, findAllById, findById, findOne, save |
| org.springframework.data.cassandra.repository.CassandraRepository | count, delete, deleteAll, deleteAllById, existsById, findAll, findAllById, findById, insert, save, saveAll |
| org.springframework.data.cassandra.repository.ReactiveCassandraRepository | count, delete, deleteAll, deleteAllById, deleteById, existsById, findAll, findAllById, findById, insert, save, saveAll |
| org.springframework.data.cassandra.repository.TypedIdCassandraRepository | count, delete, deleteAll, exists, findAll, findOne, save |
For CRUD calls, as we don’t have the text query, CAST creates a new
object called Cassandra Java Operation. The name of the object is
Select/Insert/Update/Delete, depending on the type of call. It inherits
from the following Cassandra objects and the property tableName has as
value the name of the table to which it will be linked:
- CAST_Cassandra_Select_Table
- CAST_Cassandra_Insert_Table
- CAST_Cassandra_Update_Table
- CAST_Cassandra_Delete_Table
Example of Cassandra Java Operation Update:
SensorIndexServiceImpl.java
public class SensorIndexServiceImpl implements SensorIndexService {
SensorIndexRepository sensorIndexRepository;
@Override
public SensorIndex save(final SensorIndex sensorIndex) {
return sensorIndexRepository.save(sensorIndex);
}
}
The repository Java class:
SensorIndexRepository.java
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.repository.CassandraRepository;
public interface SensorIndexRepository
extends CassandraRepository<SensorIndex, SensorIndexKey>, SensorIndexRepositoryCustom {
...
}
The table Java class:
SensorIndex.java
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.mapping.Column;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.mapping.PrimaryKey;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.mapping.Table;
@Value
@Builder(builderClassName = "Builder")
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE, force = true)
@Table("sensor_index")
public class SensorIndex {
@PrimaryKey
private final SensorIndexKey key;
@Column("value")
private final BigDecimal value;
}
The CQL file containing table creation code:
sensor_index.cql
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS sensor_index(sensor_id text, year int, ts timestamp ,value decimal, PRIMARY KEY ((sensor_id, year), ts));
The expected result:

Query method calls
Similar to CRUD calls CAST supports the query method calls. Example of Cassandra Java Operation Select:
EmployeeRepository.java
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.repository.CassandraRepository;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends CassandraRepository<Employee, Integer> {
@AllowFiltering
Flux<Employee> findByAgeGreaterThan(int age);
}
The CQL file containing table creation code:
employee.cql
CREATE TABLE employee (
id text,
name text
PRIMARY KEY ((id), name));
The expected result:

CassandraOperations and CassandraTemplate
CQL queries can be built using org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.CassandraOperations and org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.CassandraTemplate class APIs. The supported APIs are: execute, select, insert, update, delete.
Example of select query:
EmployeeRepository.java
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.CassandraOperations;
import com.datastax.driver.core.querybuilder.QueryBuilder;
import com.datastax.driver.core.querybuilder.Select;
public class IntradayWeatherRepositoryImpl implements IntradayWeatherRepositoryCustom {
@Override
public List<IntradayWeather> findByTs(int weatherStationId, Set<Integer> years, Date begin, Date end) {
final Select select = QueryBuilder.select().all().from(template.getTableName(IntradayWeather.class).toCql());
select.where(QueryBuilder.eq(WEATHER_STATION_ID, weatherStationId))
.and(QueryBuilder.in(YEAR_COLUMN_NAME, years.toArray()))
.and(QueryBuilder.gte(TEMPERATURE_TS_COLUMN_NAME, begin))
.and(QueryBuilder.lt(TEMPERATURE_TS_COLUMN_NAME, end));
return template.select(select, IntradayWeather.class);
}
}
The CQL file containing table creation code:
intraday_weather.cql
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS intraday_weather(weather_station_id int, year int, temperature_ts timestamp,production_ts timestamp,temperature decimal, pictogram text, PRIMARY KEY ((weather_station_id, year), temperature_ts));
The expected result:

Example of insert query:
CassandraApplication.java
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.CassandraOperations;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.CassandraTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.query.Criteria;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.query.Query;
import com.datastax.oss.driver.api.core.CqlSession;
public class CassandraApplication {
private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(CassandraApplication.class);
private static Person newPerson(String name, int age) {
return new Person(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), name, age);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CqlSession cqlSession = CqlSession.builder().withKeyspace("mykeyspace").build();
CassandraOperations template = new CassandraTemplate(cqlSession);
Person jonDoe = template.insert(newPerson("Jon Doe", 40));
cqlSession.close();
}
}
Person.java
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.mapping.PrimaryKey;
import org.springframework.data.cassandra.core.mapping.Table;
@Table
public class Person {
@PrimaryKey private final String id;
private final String name;
public Person(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
private String getName() {
return name;
}
}
The CQL file containing table creation code:
Person.cql
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Person(id int, name text);
The expected result:

CqlTemplate
CQL queries can be built using org.springframework.cassandra.core.CqlTemplate class APIs.
The supported APIs are: execute, query, queryForObject, queryForList.
Example of queryForObject and execute APIs.
Example.java
import org.springframework.cassandra.core.CqlTemplate;
public class Example {
private static CqlTemplate cqlTemplate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int countOfActorsNamedJoe = cqlTemplate.queryForObject(
"SELECT COUNT(*) FROM t_actor WHERE first_name = ?", Integer.class);
cqlTemplate.execute("CREATE TABLE t_actor (id uuid primary key, first_name text)");
}
}
The expected results:


Database access with DataStax
Supported DataStax Classes
| Example of main DataStax classes used for table access |
|
|---|
The APIs com.datastax.oss.driver.api.querybuilder.QueryBuilder and com.datastax.oss.driver.api.querybuilder.SchemaBuilder allow the generation of CQL queries programmatically for Cassandra NoSQL. There are various ways to build the queries. You can either build (com.datastax.oss.driver.api.core.cql.session.SessionBuilder.build) or execute (com.datastax.driver.core.Session.execute, com.datastax.oss.driver.core.Session.execute, com.datastax.oss.driver.api.core.CqlSession.execute) these queries.
Tables are created either via *.cql files, and in this case, as in the example above, we have Cassandra CQL Table objects, either programmatically in java via queries. In the second case, we have Cassandra Java Table objects.
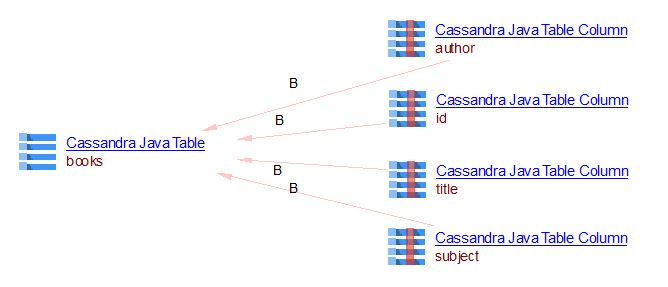
Example of Create Table Query in Java with StringBuilder API
BookRepository.java
public class BookRepository {
private static final String TABLE_NAME = "books";
private Session session;
public BookRepository(Session session) {
this.session = session;
}
public void createTable() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ").append(TABLE_NAME).append("(").append("id uuid PRIMARY
KEY, ").append("title text,").append("author text,").append("subject text);");
final String query = sb.toString();
session.execute(query);
}
...
}
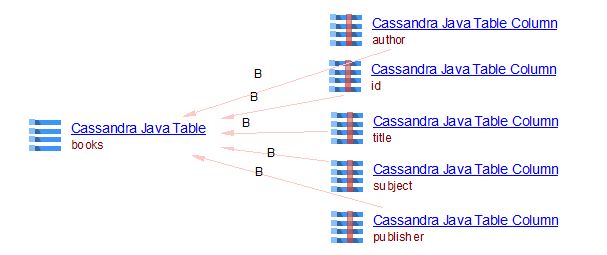
The expected result:


Example of Select Query in Java with StringBuilder API
BookRepository.java
public class BookRepository {
private static final String TABLE_NAME = "books";
private Session session;
public BookRepository(Session session) {
this.session = session;
}
public List<Book> selectAll() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("SELECT * FROM ").append(TABLE_NAME);
final String query = sb.toString();
ResultSet rs = session.execute(query);
List<Book> books = new ArrayList<Book>();
for (Row r : rs) {
Book book = new Book(r.getUUID("id"), r.getString("title"), r.getString("author"), r.getString("subject"));
books.add(book);
}
return books;
}
...
}
The expected result:

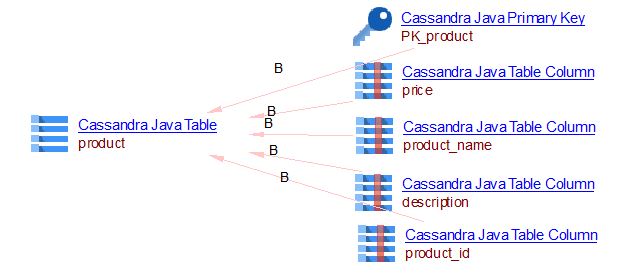
Example of Create Table in Java with SchemaBuilder API
The SchemaBuilder is an additional API provided by java driver query builder that enables generating CQL DDL queries programmatically. It is used to:
- generate schema queries based on application configuration
- generate representative schema DDL CREATE queries, given a Java class that represents a table, view, or user defined type.
ProductRepository.java
public class ProductRepository {
private static final String PRODUCT_TABLE_NAME = "product";
private final CqlSession session;
public ProductRepository(CqlSession session) {
this.session = session;
}
public void createProductTable(String keyspace) {
CreateTable createTable = SchemaBuilder.createTable(PRODUCT_TABLE_NAME).ifNotExists()
.withPartitionKey("product_id", DataTypes.UUID)
.withColumn("product_name", DataTypes.TEXT)
.withColumn("description", DataTypes.TEXT)
.withColumn("price", DataTypes.FLOAT);
executeStatement(createTable.build(), keyspace);
}
private ResultSet executeStatement(SimpleStatement statement, String keyspace) {
if (keyspace != null) {
statement.setKeyspace(CqlIdentifier.fromCql(keyspace));
}
return session.execute(statement);
}
}
The expected result:

Example of Create keyspace in Java with SchemaBuilder API
Following table creation example, keyspace are created (Cassandra Java Schema objects).
KeyspaceRepository.java
public class KeyspaceRepository {
private final CqlSession session;
public KeyspaceRepository(CqlSession session) {
this.session = session;
}
public void createKeyspace(String keyspaceName, int numberOfReplicas) {
CreateKeyspace createKeyspace = SchemaBuilder.createKeyspace(keyspaceName)
.ifNotExists()
.withSimpleStrategy(numberOfReplicas);
session.execute(createKeyspace.build());
}
}
CassandraClient.java
public class CassandraClient {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CassandraClient.class);
public static void main(String args[]) {
CassandraConnector connector = new CassandraConnector();
connector.connect("127.0.0.1", null);
Session session = connector.getSession();
KeyspaceRepository sr = new KeyspaceRepository(session);
sr.createKeyspace("library", 1);
sr.useKeyspace("library");
}
}
The expected result:


Example of Alter Table in Java with SchemaBuilder API
BookRepository.java
public void alterTable(String keyspace) {
BuildableQuery alterTable = SchemaBuilder.alterTable("books")
.alterColumn("publisher", DataTypes.Text);
executeStatement(alterTable.build(), keyspace);
}
The expected result:

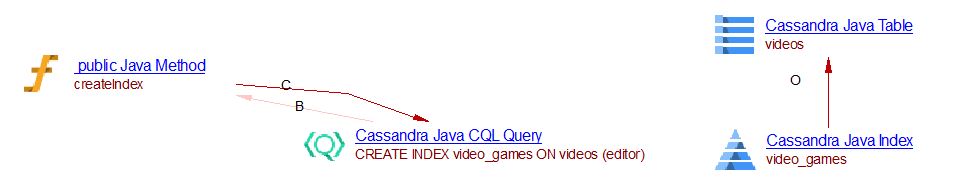
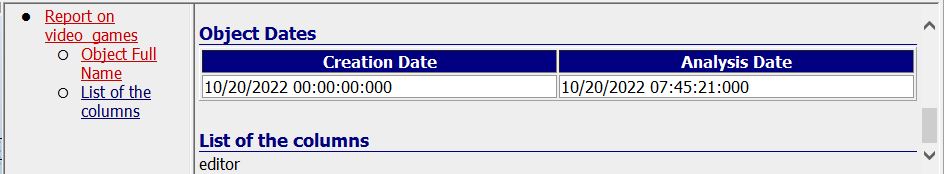
Example of Create Index in Java with SchemaBuilder API
KeyspaceRepository.java
public void createIndex() {
CreateIndex index = SchemaBuilder.createIndex("video_games")
.ifNotExists()
.onTable("videos")
.andColumn("editor");
session.execute(index.build());
}
The expected result: