SQL Analyzer - 3.7
Extension ID
com.castsoftware.sqlanalyzer
What’s new ?
See Release Notes.
Description
The SQL Analyzer provides support for database technologies using the ANSI SQL-92/99 language. This extension uses the Universal Analyzer framework and is intended to analyse DDL, DML and SQL exports for a large variety of SQL variants:
- This extension provides source code analysis support for DDL and DML source files using an over language of the various SQL variants.
- See Supported File Extensions below for the list of supported files.
In what situation should you install this extension?
- If you need to analyze the SQL server part compliant with ANSI SQL-92 / 99 of your client/server application
Transitioning from from the CAST AIP Db2 Analyzer to the SQL Analyzer extension
If you have been actively analyzing Db2 (z/OS or LUW) with the Db2 Analyzer (provided out-of-the-box in CAST AIP) you can transition to using the SQL Analyzer extension to analyze your Db2 source code. The process of transitioning is described in SQL Analyzer - To do transition from the CAST AIP Db2 Analyzer to the SQL Analyzer extension.
Reversed links
When transitioning from the Db2 Analyzer to the SQL Analyzer, links between Tables and Indexes, Foreign Keys, Primary Keys and Unique Keys will appear to be reversed when comparing the analysis results of the Db2 Analyzer and the SQL Analyzer. This is because the representation of links in the SQL Analyzer uses a different method (which is identical for all supported RDBMS) to the Db2 Analyzer.
Transitioning from the CAST AIP Oracle Analyzer to the SQL Analyzer extension
If you have been actively analyzing Oracle with the Oracle Analyzer (provided out-of-the-box in CAST AIP) you can transition to using the SQL Analyzer extension to analyze your Oracle source code. The process of transitioning is described in SQL Analyzer - To do transition from the CAST AIP Oracle Analyzer to the SQL Analyzer extension.
Analyzing the same code will generate differences in results across object types, object links and structural rules. If you do decide to move to the SQL Analyzer extension, see SQL Analyzer - Mapping between SQL analyzers for more information about what you can expect.
Important! Don’t change analyzed sources, keep analyzing src files. Only GUIDs are changed during transitions, checksums are recalculated, and that will impact transactions.
Oracle Forms and Reports particular case
- If you have already analyzed Oracle Forms and Reports code that is linked to PL/SQL code analyzed with the SQL analyzer embedded in CAST AIP, CAST recommends that you continue using the SQL analyzer embedded in CAST AIP.
Transitioning from the CAST AIP SQL Server Analyzer to the SQL Analyzer extension
If you have been actively analyzing MS SQL Server with the MS SQL Server Analyzer (provided out-of-the-box in CAST AIP) you can transition to using the SQL Analyzer extension to analyze your SQL Server source code. The process of transitioning is described in How to do transition from the CAST MS SQL Server Analyzer to the SQL Analyzer extension.
Analyzing the same code will generate differences in results across object types, object links and structural rules. If you do decide to move to the SQL Analyzer extension, see SQL Analyzer - Mapping between SQL analyzers for more information about what you can expect.
Important! Don’t change analyzed sources, keep analyzing src files. Only GUIDs are changed during transitions, checksums are recalculated, and that will impact transactions.
Transitioning from the CAST AIP ASE Sybase Analyzer to the SQL Analyzer extension
If you have been actively analyzing ASE Sybase with the ASE Sybase Analyzer (provided out-of-the-box in CAST AIP) you can transition to using the SQL Analyzer extension to analyze your ASE Sybase source code. The process of transitioning is described in SQL Analyzer - To do transition from the CAST AIP ASE Sybase Analyzer to the SQL Analyzer extension.
Analyzing the same code will generate differences in results across object types, object links and structural rules. If you do decide to move to the SQL Analyzer extension, see SQL Analyzer - Mapping between SQL analyzers for more information about what you can expect.
Important! Don’t change analyzed sources, keep analyzing src files. Only GUIDs are changed during transitions, checksums are recalculated, and that will impact transactions.
Supported file extensions
The following table summarizes the source file extensions managed by the SQL Analyzer by default. Other file extensions could be used, upon manual configuration (within CAST Console). You can also have a look to Database File Discovererin order to understand which one of the file extensions are taken in account when a SQL project is added.
File |
Extension |
Mandatory/Optional | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL source files | .sql .sqlt .ddl .dml .plsql .pgsql .mysql |
Mandatory |
DDL / DML files You should deliver at least one of the listed extensions.
|
| CAST generated Files | .uaxdirectory .src |
.src files are SQL sources files generated with CAST Database Extractor. Supported for compatibility reasons only. |
|
| IBM Db2 for i Logical File | .lf .lf38 |
IBM Db2 for i View in DDS format | |
| IBM Db2 for i Physical File | .pf .pf38 |
IBM Db2 for i Table in DDS format | |
| CAST SQL Table Size File | .sqltablesize | Optional | See SQL Analyzer - working with XXL or XXS tables. |
| CAST Data Sensitive File | .datasensitive | Optional | See SQL Analyzer - RDBMS Table Sensitive Data. |
| Additional SQL source files | .bdy .db2 .fnc .pck .pkb .pkg .pks .plb .pls .spc .tab .tpb .tps .trg .trigddl .tsql .udf .viewddl .viw .vw |
Optional | DDL files Those files are not recognised by Database File Discoverer but if you have at least one mandatory file in the analysis root folder, the SQL Analyzer will analyze them. |
Unsupported files extensions
Some other file extensions could potentially have SQL statements, e.g. : *.inc, *.prc or *.vue. The product is matching them with PHP language for *.inc, JCL language for *.prc and VueJS for *.vue. That’s why they are not listed above. If you’re sure they contains valuable SQL statements, simply change the extension from inc/prc/vue to sql.
Vendor compatibility matrix - official support
| Icon | Vendor | Version | Supported? |
|---|---|---|---|
|
IBM Db2 for LUW | Up to version 11.x |
|
|
IBM Db2 for z/OS | Up to version 12 | |
|
IBM Db2 for i | Up to version 7.5 | |
|
IBM Informix | Up to version 14.x | |
|
MariaDB | Up to version 10.x | |
|
Microsoft SQL Server | Up to version 2022 | |
|
MySQL | Up to version 8.x | |
|
Oracle Server | Up to version 23ai | |
|
PostgreSQL | Up to version 17.x | |
|
SAP ASE (formerly known as Sybase ASE) | Up to version 16 | |
|
SQLite | Up to version 3.x | |
|
Teradata | Up to version 16 | |
|
CockroachDB | Up to version 24 | |
|
NonStop SQL | Up to version 3.x |
*) added in 3.6.0-beta1
Function Point, Quality and Sizing support
- Function Points (transactions): a green tick indicates that OMG Function Point counting and Transaction Risk Index are supported
- Quality and Sizing: a green tick indicates that CAST can measure size and that a minimum set of Quality Rules exist
| Function Points (transactions) | Quality and Sizing |
|---|---|
| ✅ | :white_check_mark |
Compatibility
| Release | Operating System | Supported |
|---|---|---|
| v3/8.4.x | Microsoft Windows / Linux | ✅ |
| v2/8.3.x | Microsoft Windows | ✅ |
What results can you expect?
Once the analysis/snapshot generation has completed, you can view the results in the normal manner (for example via CAST Enlighten) - click to enlarge:
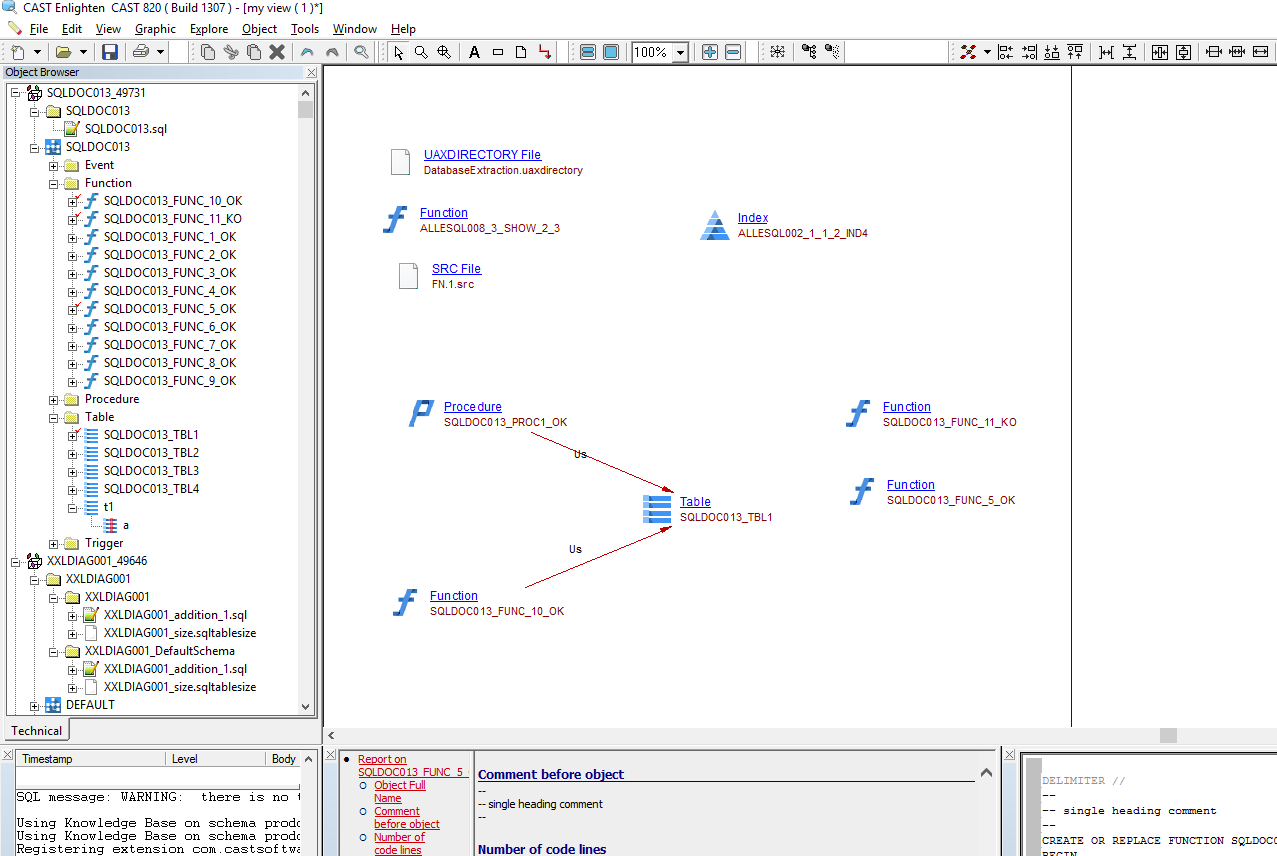
You can also use the CAST Management Studio option View Analysis Unit Content to see the objects that have been created following the analysis:
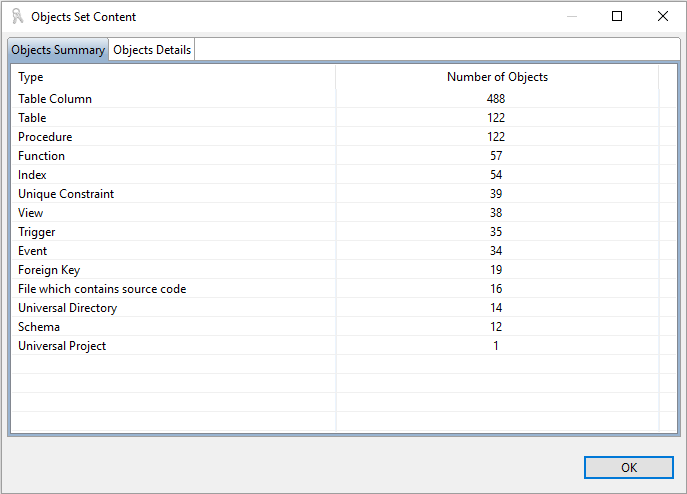
Objects
| Icon | Object Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |
Database | Objects created for MS SQL Server, ASE Sybase, IBM Db2, CockroachDB and NonStop SQL, see details about how database is determined here: SQL Analyzer - How object identity is determined |
 |
Schema | Objects created for all RDBMS, see details about how schema is determined here : SQL Analyzer - How object identity is determined |
 |
Table | Objects created with CREATE TABLE statements. Records in *.pf *.pf38 files, specific to Db2fori variant. Table name is given by the file name. |
 |
View | Objects created with CREATE VIEW / REPLACE VIEW statements. Records in *.lf *.lf38 files, specific to Db2fori variant. View name is given by the file name. |
 |
Table Column | Columns detected in CREATE TABLE statements. For CREATE VIEW statements only aliases, the names for the expressions selected by the defining query of the view, are considered as columns names. |
 |
Index | Objects created with CREATE INDEX statements. |
 |
Foreign Key | Objects created with CREATE TABLE … (… FOREIGN KEY ..) / ALTER TABLE …. FOREIGN KEY … statements. |
 |
Unique Constraint | Objects created with CREATE UNIQUE INDEX or CREATE PRIMARY KEY statements. For the CREATE PRIMARY KEY / ALTER TABLE ADD CONSTRAINT PRIMARY KEY / ALTER TABLE ADD PRIMARY KEY / CREATE TABLE …. ( … PRIMARY/UNIQUE KEY …) statements, tables are marked as having a primary key. Key in *.pf *.pf38 files, specific to Db2fori variant. Unique constraint name is given by the file name prefixed with PK_. |
 |
Trigger | Objects created with CREATE TRIGGER / CREATE RULE statements. |
 |
Event | Objects created with CREATE EVENT statements. |
 |
Macro | Objects created with CREATE MACRO statements. |
 |
Package | Objects created with CREATE PACKAGE/PACKAGE BODY statements. |
 |
Procedure | Objects created with CREATE PROCEDURE / REPLACE PROCEDURE statements. The same type cover Package’s procedures. |
 |
Function | Objects created with CREATE FUNCTION statements. The same type cover Package’s functions. |
 |
Type | Objects created with CREATE TYPE/TYPE BODY statements. |
 |
Method | Object Type’s methods. |
 |
Synonym | Object created with CREATE SYNONYM, CREATE ALIAS, CREATE SQLMP ALIAS and CREATE NICKNAME statements. |
 |
Database Link | Object created with CREATE DATABASE LINK statements. |
 |
Unresolved Schema | When objects accessed via a Database Link in a DML statement are not resolved, they are missing from analysis result, an Unresolved table or Unresolved Object is created, in a Unresolved Schema. When the object is more “table like”, we add an Unresolved Table. When the object is more “procedure / function like” we add an Unresolved Object. In the Database Link, access objects are prefixed with schema name, that schema will belongs to the Database Link object, Unresolved Table / Object will belongs to Unresolved Schema. See example SQL Analyzer - How object identity is determined. |
 |
Unresolved Table | As above |
 |
Unresolved Object | As above |
 |
DML Script File | File with DML SQL statements, like INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE/etc. DML Script File candidates with more than 80% INSERT statements are considered as data exports and will not be analyzed. Sometimes DML and DDL statements are mixed and DML Script Files are also considered as DDL. |
 |
sourceFile | This is a logical file. For each source file we add a property named Vendor, see SQL file Vendor - This file is analyzed against XXX variant. |
Table deletion and renaming
DROP TABLE syntax is supported for table objects within the same file. When creating a table through CREATE TABLE tableName (colName int, …) followed by a DROP TABLE tableName, the table will not be recorded and thus will not be displayed in CAST Enlighten. Similarly, if a table is renamed with a RENAME TABLE statement (or ALTER TABLE RENAME TO as in SQLite and PostgreSQL), this change will be reflected in CAST Enlighten. Presently we consider case-insensitive names, i.e., objects named tableName, TABLEname are considered to be the same object.
Database object
Db2 analyses
Please read this note if you move from sqlanalyzer <= 2.6.9-funcrel to sqlanalyzer >= 3.0.0-alpha2 and if the AIP core is from 8.3.16 to 8.3.28: SQL Analyzer - Upgrading SQL Analyzer when AIP core is from 8.3.16 to 8.3.28.
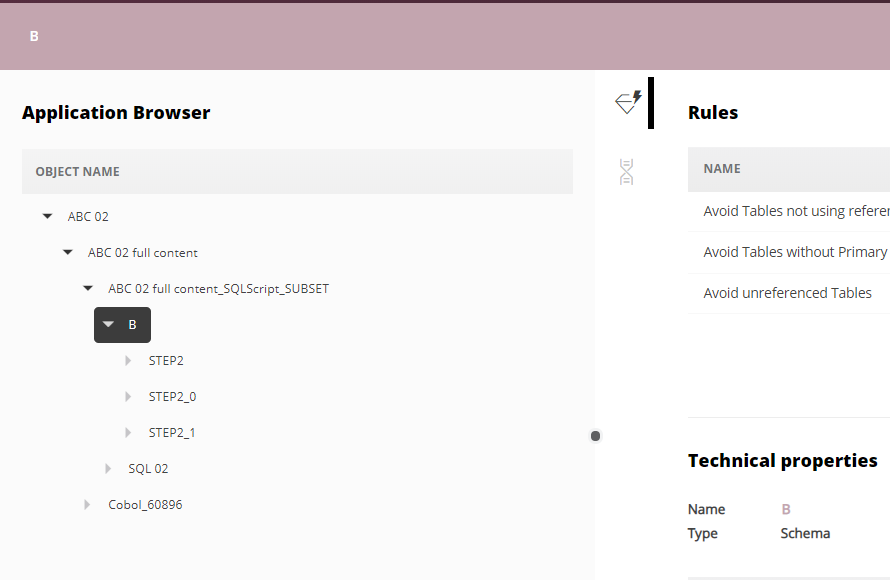
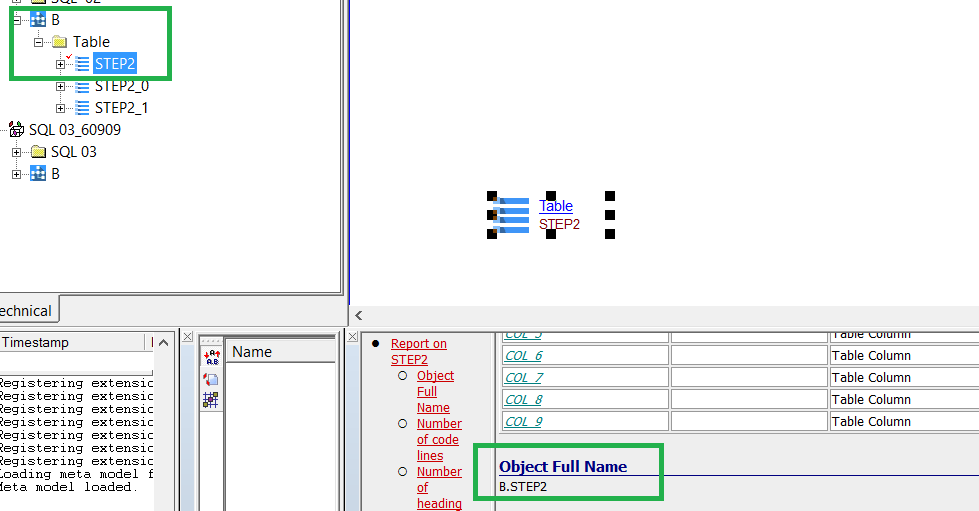
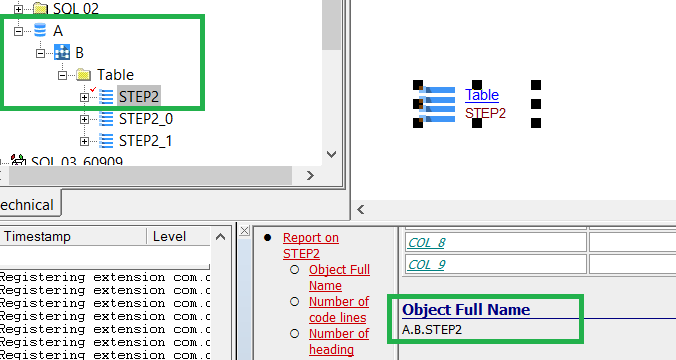
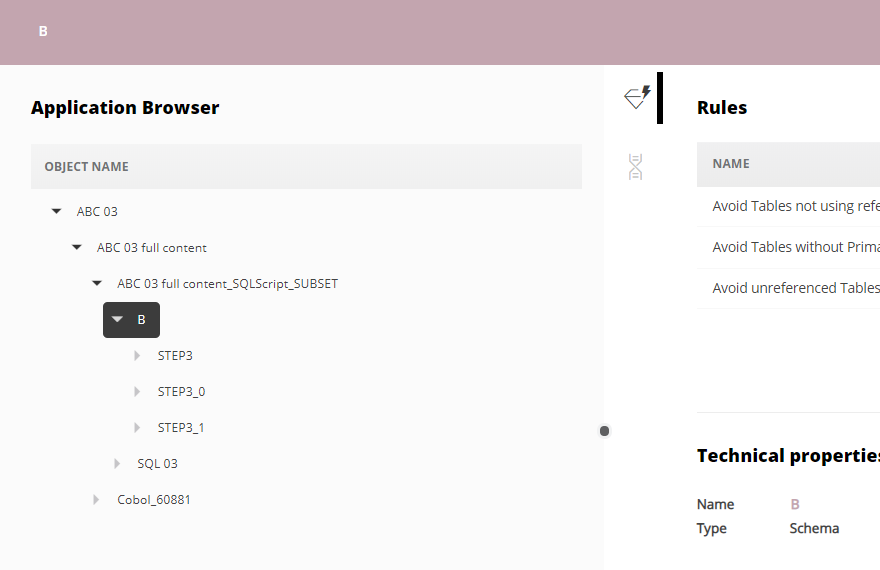
The following CREATE TABLE … IN … statements will generate a new object: a database for Db2 analyses:
CREATE TABLE .... () ... IN DATABASE_NAME.TABLESPACE_NAME .... --see ABC 02 example
CREATE TABLE .... () IN DATABASE DATABASE_NAME --see ABC 03 example
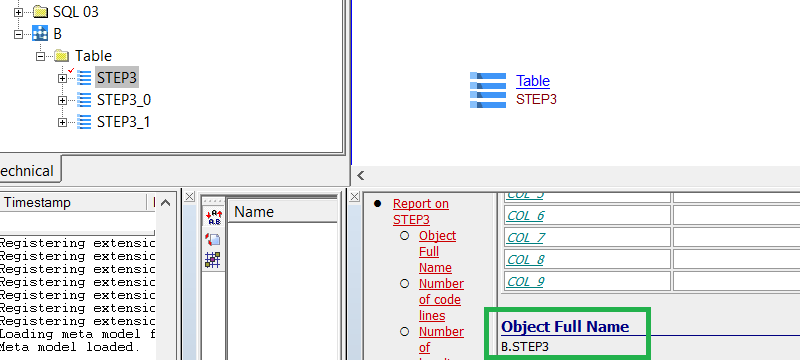
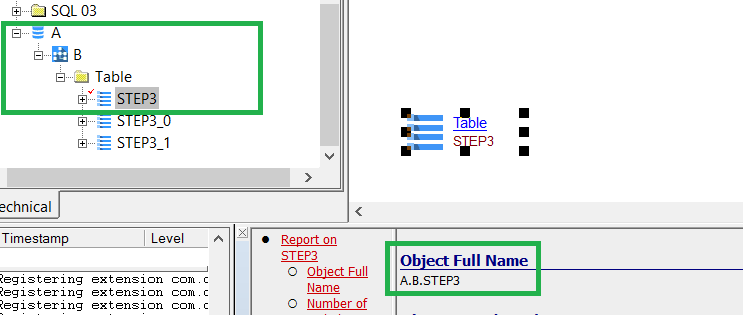
Object Full Name will change from <SCHEMA NAME>.<OBJECT NAME> to <DATABASE NAME>.<SCHEMA NAME>.<OBJECT NAME:
| prior to 3.0.0-alpha2 | 3.0.0-alpha2 |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SQL Server analyses
Please read this note if you move from sqlanalyzer < 3.4.0-beta5 to sqlanalyzer >= 3.4.0-beta5 and if the AIP core is from 8.3.16 to 8.3.28: SQL Analyzer - Upgrading SQL Analyzer when AIP core is from 8.3.16 to 8.3.28.
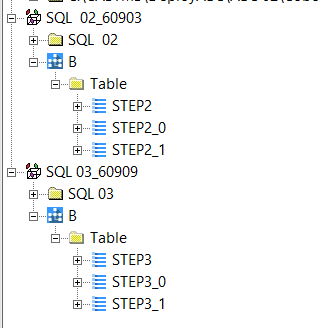
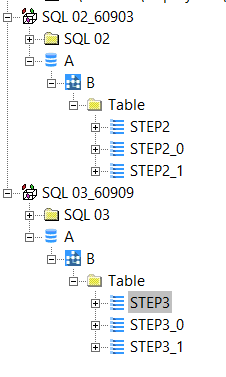
The following statements will generate a database for SQL Server and Sybase analyses:
USE <DATABASE_NAME>
CREATE DATABASE <DATABASE_NAME>
CREATE <OBJECT_TYPE>*) <DATABASE_NAME>.<SCHEMA_NAME>.<OBJECT_NAME>
*) TABLE, VIEW, etc
Object Full Name will change from <SCHEMA NAME>.<OBJECT NAME> to <DATABASE NAME>.<SCHEMA NAME>.<OBJECT NAME>.
Database Link object
Added support for CREATE DATABASE LINK statement : https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/statements_5005.htm .
The caller object is linked with Database Link object via relyOn links. The called object is directly linked to the caller object, via Use / Call links.
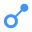
Example 1 : with a call via Database Link
Create Procedure MYPROC_DBLINK
Is
Begin
MYREMOTESCHEMA.MYREMOTEPROC@DBLINK.DOMAIN(0, 'string1');
End;
/
CREATE SHARED PUBLIC DATABASE LINK DBLINK.DOMAIN
CONNECT TO TOTO
USING 'TOTO.db.toto.com'
/
create procedure MYREMOTESCHEMA.MYREMOTEPROC(I_1 int,
I_2 varchar2(500)
as
begin
return 1;
end;
/
The caller object, MYPROC_DBLINK, is linked with :
- the Database Link object DBLINK.DOMAIN via a relyOn link
- the called object MYREMOTEPROC via a call link
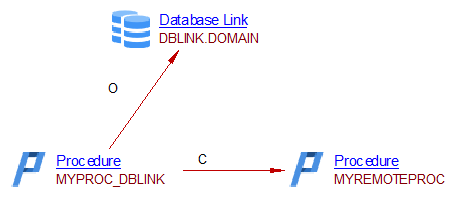
Example 2 : with a call via a synonym on a Database Link
create procedure MYREMOTESCHEMA.MYREMOTEPROC(I_1 int,
I_2 varchar2(500)
as
begin
return 1;
end;
/
CREATE SHARED PUBLIC DATABASE LINK DBLINK.DOMAIN
CONNECT TO TOTO
USING 'TOTO.db.toto.com'
/
CREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM MYPROC_SYN_DBLINK
FOR MYREMOTESCHEMA.MYREMOTEPROC@DBLINK.DOMAIN;
/
Create Procedure MYPROC_DBLINK
Is
Begin
MYPROC_SYN_DBLINK(0, 'string1');
End;
/
The caller object, MYPROC_DBLINK, is linked with the called object MYREMOTEPROC via a call link
The PUBLIC synonyms is on a procedure accessed via a Database Link and has relyOn links with Database Link DBLINK.DOMAIN and the real procedure MYREMOTEPROC .
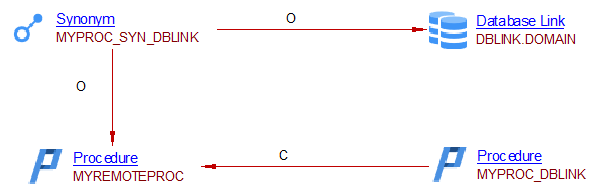
Unresolved objects
When the object accessed via a Database Link is missing, we add an Unresolved object directly attached to the Database Link.
CREATE SHARED PUBLIC DATABASE LINK DBLINK.DOMAIN
CONNECT TO TOTO
USING 'TOTO.db.toto.com'
/
Create Procedure MYPROC_UNRESOVLED_DBLINK
Is
Begin
select MYREMOTESCHEMA.MYREMOTEPROC@DBLINK.DOMAIN()
from dual;
End;
/
The caller object, MYPROC_UNRESOLVED_DBLINK, is linked with the called object MYREMOTEPROC via a call link
The PUBLIC synonyms is on a procedure accessed via a Database Link and has relyOn links with Database Link DBLINK.DOMAIN and the real procedure MYREMOTEPROC.
MYREMOTEPROC is missing from analysis result, so it is considered Unresolved.
SQL Analyzer - How object identity is determined
Oracle Public schema
Synonyms and Database Links declared as PUBLIC are attached to PUBLIC schema.
Example:
CREATE SHARED PUBLIC DATABASE LINK DBLINK.DOMAIN
CONNECT TO TOTO
USING 'TOTO.db.toto.com'
/
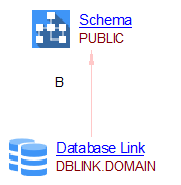
Links
Links are created for transaction and function point needs.
First table is for SQL objects created in SQL files and we call them server side links. The second is for queries from the different client languages and we call them client server links.
Server side links
| Link Type | Caller type | Callee type | Details / Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| useSelect, useUpdate, useDelete, useInsert | Procedure, Function, Macro, Event, View, DML Script File | Table, View, Synonym | |
| callLink | Procedure, Function, Event, Macro, View, DML Script File | Procedure, Function, Synonym | |
| callLink | Procedure, Function | Cobol Program | For a Procedure / Function implemented in Cobol (language COBOL/COBOLLE): 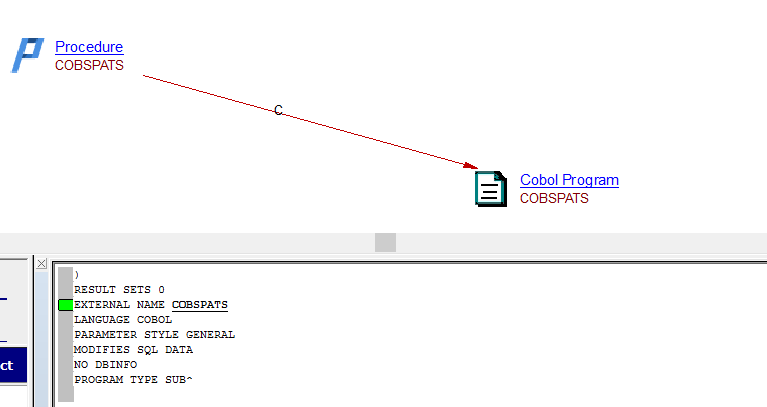 |
| callLink | Procedure, Function | C/C++ Function | For a Procedure / Function implemented in C/C++ (language C/C++) : 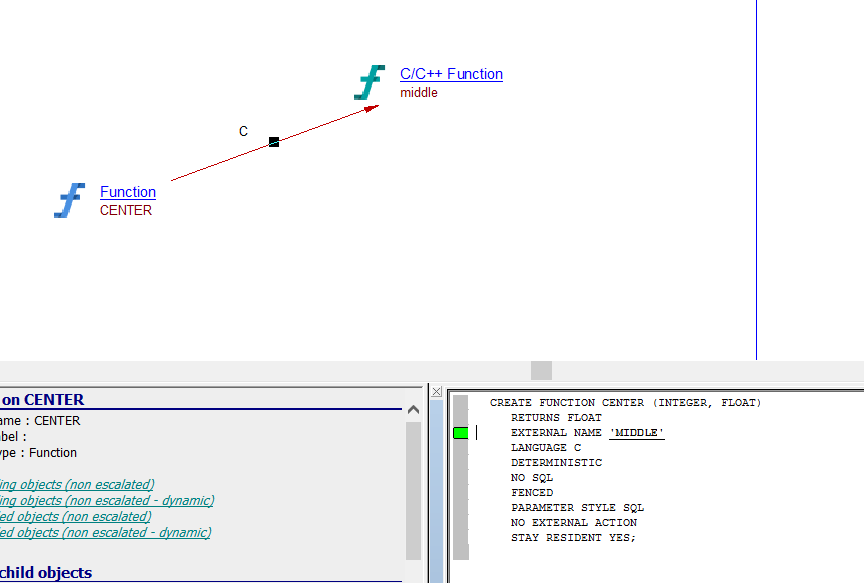 |
| callLink | Procedure, Function | Java Method | For a Procedure / Function implemented in Java (language JAVA) : 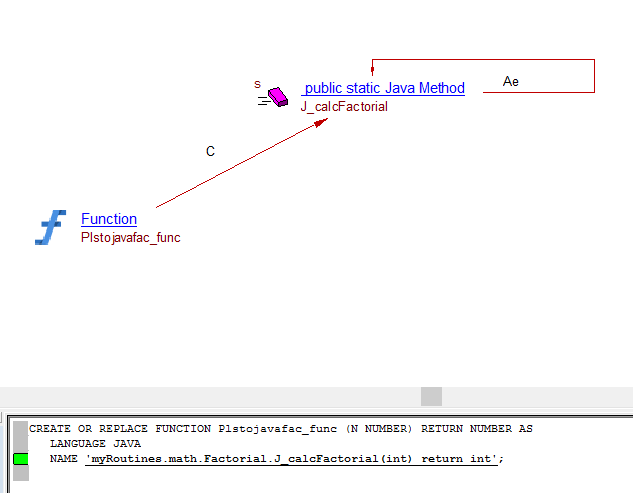 |
| callLink | Procedure, Function | RPG III Program | For a Procedure / Function implemented in RPG III (language RPG) |
| callLink | Procedure, Function | RPG IV Program | For a Procedure / Function implemented in RPG IV (language RPGLE) |
| callLink | Procedure, Function | CL Program | For a Procedure / Function implemented in CL IV (language CL) |
| callLink | Procedure, Function | PLI/PLC MainProcedure | For a Procedure / Function implemented in PL/I (language PLI) |
| callLink | Procedure, Function | Assembler Program | For a Procedure / Function implemented in Assembler (language ASSEMBLE) |
| callLink | Procedure, Function | Rexx Program | For a Procedure / Function implemented in Rexx (language REXX) |
| callLink | Method’s Type | Method’s Type | When an PL/SQL object’s method is called indirectly, via a variable. |
| callLink | Trigger | Procedure, Function | when table is INSERTED, UPDATED, DELETED in a Procedure, Function we add a call link between the Procedure, Function and the Trigger. |
| relyonLink | Index | Table | |
| relyonLink | Index | Index’s Column | |
| relyonLink | Synonym | Table, View, Function, Procedure, Package | |
| relyonLink | Type’s Method / Function / Procedure | Type, Table | When parameter/variable datatypes are PL/SQL Type/Table Columns. |
| referLink | Table, Table Column | Table, Table Column | From a Table/Table Column to a Table/Table Column referenced in a Foreign Key. |
| referUpdate | Table | Table | From a Table to the Table referenced in a Column referenced in a Foreign Key. |
| referDelete | Table | Table | From a Table to the Table referenced in a Column referenced in a Foreign Key: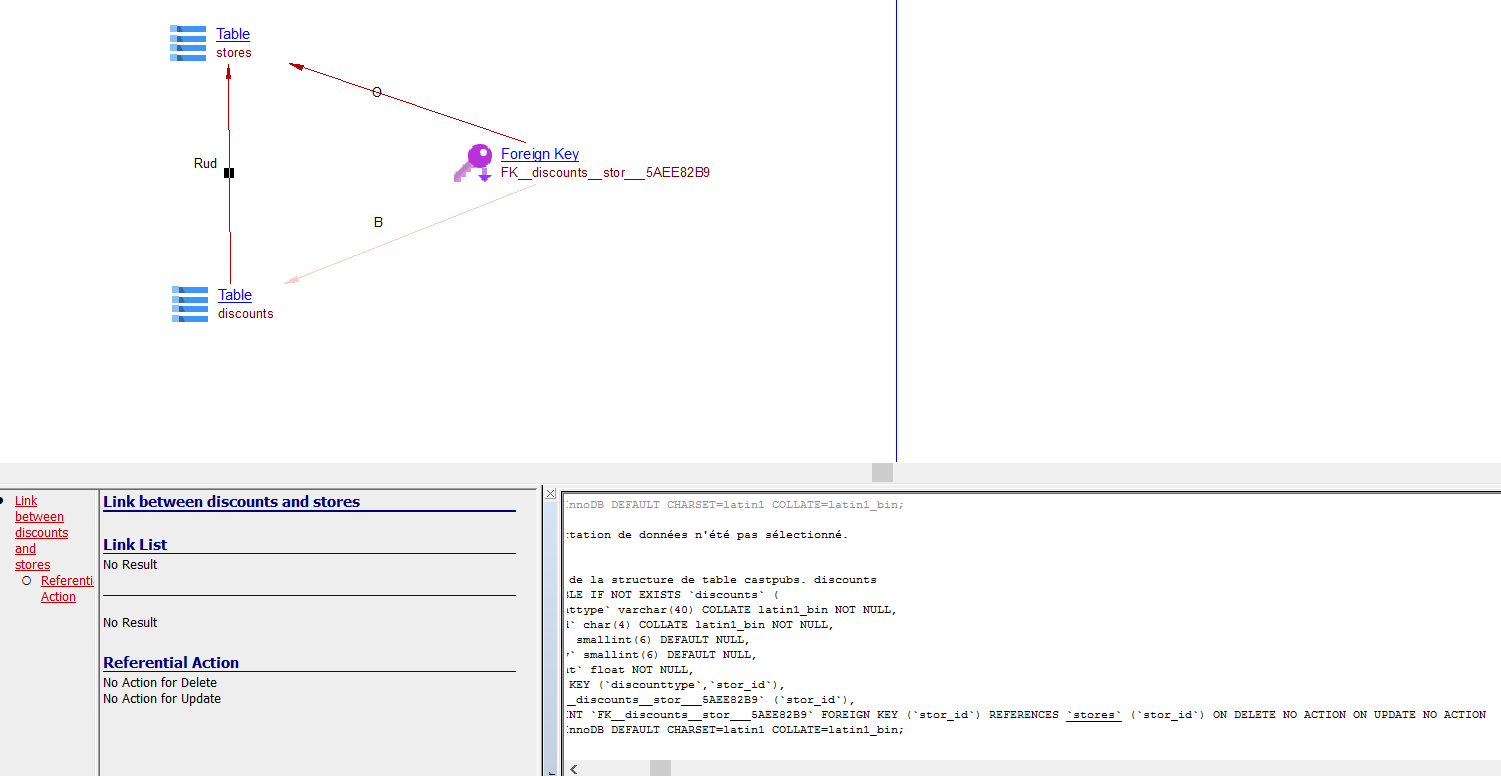 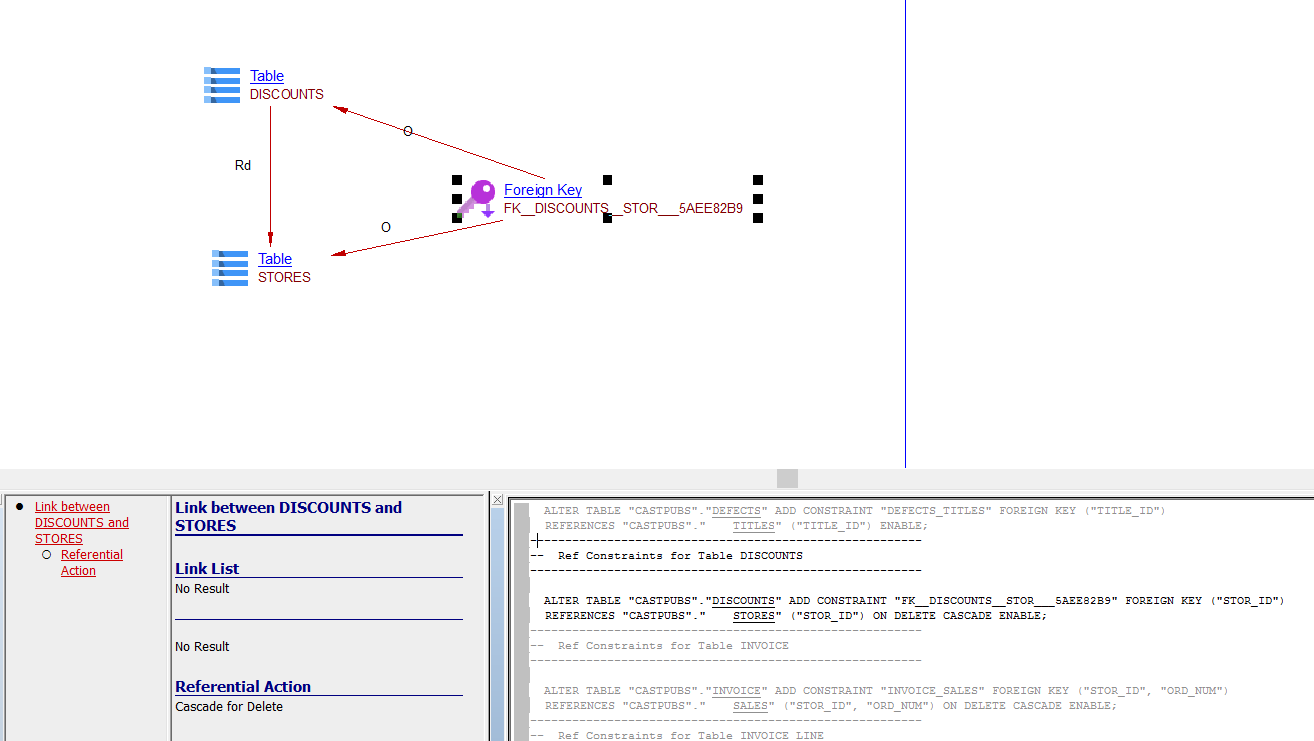 |
| callLink | DML Script File, SQL Query | Trigger | Call the Trigger when the tables are inserted/updated/deleted: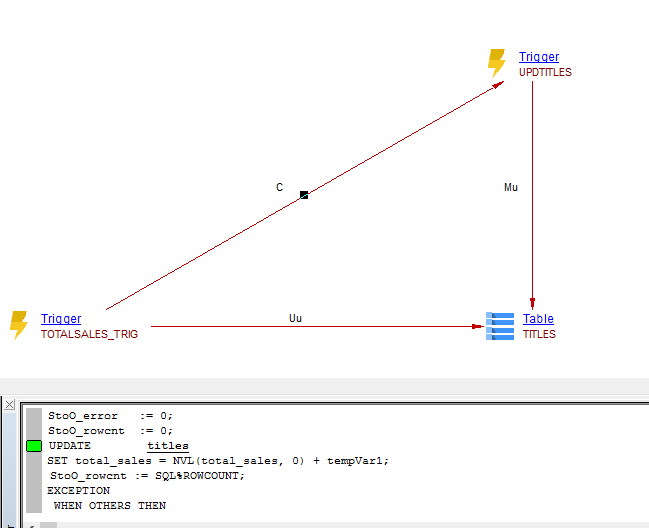 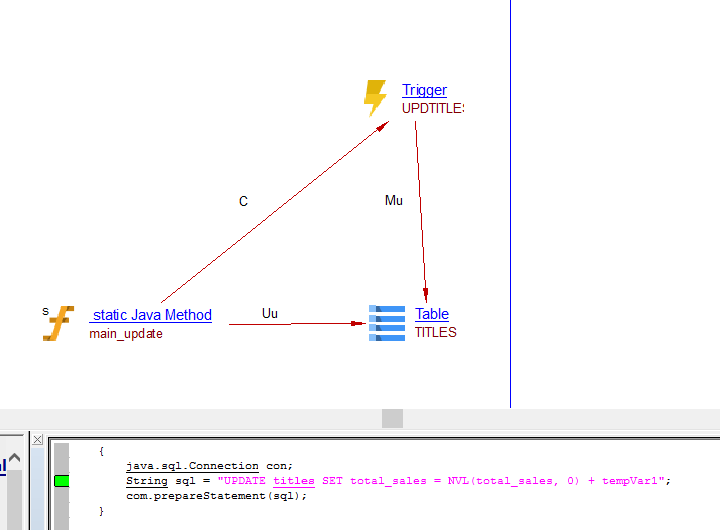 |
| inheritExtendLink | sub Type | super Type | For PL/SQL Types. |
| inheritOverrideLink | Method Type | Method Type | From a PL/SQL Method’s Type which override a super Type’s Method. |
| useLink | Type | Type | For PL/SQL tables, example:CREATE OR REPLACE TYPE "CNCUBLIST_2" is table of "HIS_TEST_A";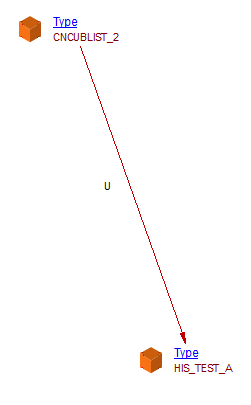 |
| monitorInsert, monitorUpdate, monitorDelete | Trigger | Table, View |
Client server links
SQL Analyzer is responsible to create the following client server links for the embedded SQL supported by Analyzers and extensions, that is through SQL Query and Entity / Entity Operations intermediate objects. This is the case of JDBC, JPA / Hibernate, EF, Ado.net, Dapper, Embeded SQL in COBOL, Pro*C, Python, NodeJS, Oracle Forms and Reports *), etc.
*) Starting with SQL Analyzer 3.7.10-funcrel.
| Link Type | Caller type | Callee type | Details / Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| useSelect, useUpdate, useDelete, useInsert | SQL Query, Java Property Mapping Query, Entity Operation |
Table, View, Synonym | SQL Query is a Client SQL Query, having the icon  . . A Java Property Mapping Query is property similar to a SQL statement. Java Property object icon is  . . Entity Operations are client objects like JPA Entity Operation, NodeJS Entity Operation, etc. If a table is selected in the Cobol / RPG SQL Query DECLARE C1 CURSOR we consider it is selected in the Cobol SQL Query FETCH C1. |
| callLink | SQL Query, Java Property Mapping Query |
Procedure, Function, Macro, Synonym | |
| callLink | Trigger | SQL Query, Java Property Mapping Query |
When table is INSERTED, UPDATED, DELETED in a SQL Query, Java Property Mapping Query we add a call link between the SQL Query, Java Property Mapping Query and the Trigger. |
| useSelect, useUpdate, useDelete, useInsert | IMS SQL Query | IMS DB Segment | |
| monitorInsert, monitorUpdate, monitorDelete | Oracle Forms Trigger | Table, View |
Rules
You can find a full list of rules delivered with this extension here:
- 3.7.13-funcrel
- 3.7.12-funcrel
- 3.7.11-funcrel
- 3.7.10-funcrel
- 3.7.9-funcrel
- 3.7.8-funcrel
- 3.7.7-funcrel
- 3.7.6-funcrel
- 3.7.5-funcrel
- 3.7.4-funcrel
- 3.7.3-funcrel
- 3.7.2-funcrel
- 3.7.1-funcrel
- 3.7.0-funcrel
- 3.7.0-beta5
- 3.7.0-beta4
- 3.7.0-beta3
- 3.7.0-beta2
- 3.7.0-beta1
Client Side Support
This section lists the analyzers that benefit from client-side support:
- a series of quality rules operating on the SQL statements extracted from the embedded SQL code : EXEC SQL blocks, Native SQL queries. This excludes pure ORM accesses where the full SQL statement is determined at runtime, thus not accessible to the analysis engine.
- Data Column Access enablement, for links and sensitive data feature.
| Analyzer | Embedded SQL Query icon | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mainframe Analyzer (COBOL) Mainframe Analyzer (IMS) Mainframe Analyzer (JCL) RPG Analyzer (RPG and CL) JEE Analyzer .NET Analyzer Node.js Python HTML5/Javascript Typescript and frameworks Business Intelligence and Reporting Tools Apache Camel Oracle Forms and Reports |
 |
These analyzers, or, for JEE and .Net, the dedicated extensions (JDBC, Persistence Frameworks, Spring Data, … Entity, ADO.Net, Dapper, …) do produce various SQL Query objects and various Entity / Entity Operations objects. |
| C/C++ (Pro*C) |  |
Queries extracted from EXEC SQL embedded SQL |
| PowerBuilder (PB) | N/A | - |
| Visual Basic (VB) | N/A | ADO, DAO, RDO |
| DML Script File |  |
Delivered as .sql, .dml, … source files |
The quality rules are calculated on the client side on the SQL Query objects, even when there is no SQL Analyzer database / schema. From a technical point of view, the following list of Embedded SQL Queries are supported:
| Embedded SQL Queries | Details / Comments |
|---|---|
| SQL Queries | CAST_SQL_MetricableQuery.sqlQuery on objects which inherit from the category CAST_SQL_MetricableQuery. SQL Query is a Client SQL Query, having the icon  . . |
| Java Property Mapping Queries | CAST_JEE_MappingProperties.mapValue on Java Property Mapping objects. A Java Property Mapping objet is a Java object having the icon  . . |
| Inference Engine Queries | physicalLink.inferenceEngineRequests on Inference Engine links |
Quality rules:
Name
|
Calculated only when we have SQL Analyzer database / schema |
|---|---|
| Never use SQL queries with a cartesian product (SQL) (1101000) | |
| Never use SQL queries with a cartesian product on XXL Tables (SQL) (1101002) | |
| Avoid non-indexed SQL queries (1101004) | |
| Avoid non-indexed XXL SQL queries (1101006) | |
| Avoid non-SARGable queries (1101008) | |
| Avoid NATURAL JOIN queries (1101010) | |
| Specify column names instead of column numbers in ORDER BY clauses (1101012) | |
| Avoid queries using old style join convention instead of ANSI-Standard joins (SQL) (1101014) | |
| Avoid using the GROUP BY clause (1101018) | |
| Always define column names when inserting values (1101026) | |
| Use MINUS or EXCEPT operator instead of NOT EXISTS and NOT IN subqueries (1101028) | |
Avoid exists and not exists independent clauses (SQL) (1101032) |
|
Avoid using DISTINCT in SQL SELECT statements (1101034) |
|
Use ANSI standard operators in SQL WHERE clauses (EMBEDDED SQL) (1101036) |
|
Avoid OR conditions testing equality on the same identifier in SQL WHERE clauses (1101038) |
|
| Avoid mixing ANSI and non-ANSI JOIN syntax in the same query (1101058) | |
| Avoid using LIKE conditions starting with a wildcard character (1101060) | |
| Avoid improperly written triangular joins with XXL tables (1101066) | |
| Avoid explicit comparison with NULL (1101070) | |
| Avoid not aliased Tables (1101072) | |
| Avoid Tables aliases ending with a numeric suffix (1101074) | |
| Avoid unqualified column references (1101076) | |
| Avoid using LIKE conditions without wildcards (1101102) | |
| Avoid Cobol SQL Cursors without FOR READ ONLY or FOR FETCH ONLY or FOR UPDATE clauses (EMBEDDED SQL) (1101108) | |
| Avoid LOCK TABLE statements in SQL code for COBOL Programs (1101112) |
Special note about XXL/XXS support
See Working with XXL or XXS tables.
Special notes about Quality Rules on client side
Some Quality Rules are calculated on SQL queries on the client-side with some limitations:
- Quality Rules will be enabled on client-side code only if the server-side code has been analyzed with SQL Analyzer extension.
- For Java client-side code, SQL statements used in parameters of methods including a SQL parametrization rule are analyzed.
Example of call to a parametrized method
class Foo
{
final static String TABLE_NAME = "Person";
void method()
{
String query = "select * from " + this.TABLE_NAME;
java.sql.Statement.execute(query );
}
}
- But ‘queries’ visible in the DLM (that need reviewing) are not analyzed:
Example of a query visible in the DLM
class Foo
{
// not passed to an execute something
private final static String text = "select name from Person";
}
-
Explicit queries used in an ORM context are analyzed (or not) based on if they are visible in Enlighten
-
The following types of queries are analyzed:
- COBOL EXEC SQL
- RPG/CL
- Pro*C
-
SQL queries found in Python code are analyzed
-
SQL queries found in .properties (Java Property Mapping objects) are analyzed
Special note about redundant Quality Rules
Please see SQL Analyzer - Redundant Quality Rules not included in the SQL Analyzer.
LOC - Line of Code Counting in SQL Analyzer
LOC (Line of Code) values reported by the CAST Dashboards are specifically and only for files that are classed by CAST as “sourceFiles” (File which contains source code), with the ID 1000007. LOC values are not reported for objects.
Errors and warning
Please see Log messages for the full list of analysis errors and warnings.
Known limitations and issues
Installation
If you encounter the following error in CAST Server Manager while installing the SQL Analyzer extension, please perform the workaround described here and then attempt the installation again. This error may occur if you have installed a very old and unsupported custom Universal Analyzer language pack that used the same metamodel type names as used in the official SQL Analyzer extension.
SQL Analyzer is incompatible with the schema metamodel. It is generally due to an extension that has changed its ids.
Analysis
- All name resolution is considered as case insensitive: this may produce erroneous links on a case insensitive platform ‘playing with case’: two different tables with the same case insensitive name will be both called
- Procedure resolution handles overriding when the number of parameters are matched or number and optionals are matched. Otherwise, when calling an overridden procedure, all overrides will be called. Below are some examples here is a single call Link, between the second func1 and func2:
Match number of parameters
CREATE FUNCTION func1() RETURNS integer AS
begin
DELETE FROM table1 WHERE ID in (SELECT ID FROM table2);
end;
CREATE FUNCTION func1(mode integer) RETURNS integer AS
begin
DELETE FROM table1 WHERE ID (SELECT ID FROM table2);
end;
CREATE FUNCTION func2(mode integer) RETURNS integer AS
begin
select func1 (mode);
end;
Match number of parameters and how many are optionals
CREATE FUNCTION func1(i_mode integer) RETURNS integer AS
begin
DELETE FROM table1 WHERE ID in (SELECT ID FROM table2);
end;
CREATE FUNCTION func1(mode integer := 1) RETURNS integer AS
begin
DELETE FROM table1 WHERE ID in (SELECT ID FROM table2);
end;
CREATE FUNCTION func2(mode integer) RETURNS integer AS
begin
select func1 ();
end;
- Dynamic SQL statements are resolved when:
-
the SQL statement is readable, even for sliced statements.
-
TABLE1, TABLE2, TABLE3 and TABLE4 are visibles and useSelect link were be added
-
CREATE PROCEDURE test
AS
L_QryStr varchar2(4000);
begin
L_QryStr := 'select S.COL1, P.COL2, P.COL3, P.COL4, P.COL5, ' ||
' P.COL6, B.COL7, R.COL8, B.COL9, B.COL10' ||
' from TABLE1 S, TABLE2 P, TABLE3 B, ' ||
' ( select distinct R.COL1, R.COL2 ' ||
' from TABLE4 R ' ||
' where R.COL3 = 99999 ';
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE L_QryStr;
end;
/
-
- test_table is visible and useDelete link is added:
CREATE PROCEDURE test
AS
begin
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'truncate table test_table';
end;
/
-
- test_table is visible and useDelete link is added:
CREATE PROCEDURE test
AS
L_QryStr varchar2(4000);
begin
L_QryStr := 'truncate table ';
L_QryStr := L_QryStr || ' test_table ';
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE L_QryStr;
end;
/
-
- table name is valued via a variable which could be resolved.
- emp table is visible and useSelect link will be added
CREATE PROCEDURE test
AS
emp_rec emp%ROWTYPE;
sql_stmt VARCHAR2(200);
begin
sql_stmt := 'SELECT * FROM || emp_rec.T1 || WHERE job = 1';
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE sql_stmt;
end;
/
-
- emp table is visible and useSelect link will be added
CREATE OR REPLACE package body test_package as
type T_1 is table of varchar2(22);
emp_rec emp%ROWTYPE;
PROCEDURE test
is
sql_stmt VARCHAR2(2000);
emp_tab VARCHAR2(200);
begin
emp_tab := emp_rec;
sql_stmt := 'SELECT * FROM || emp_tab || WHERE job = :j';
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE sql_stmt;
end test;
end;
/
-
- OPEN-FOR-USING : emp table and test procedure are linked by a use SELECT link
create table emp (col1 int);
/
CREATE OR REPLACE type body test_body as
type t_emp is table of t_table index by varchar2(22);
emp_rec emp%ROWTYPE;
member PROCEDURE test(o_cursor OUT my_cursor)
IS
BEGIN
OPEN o_cursor FOR
'SELECT rule_id,
expression_id,
parent_expression_id,
operator
FROM emp
ORDER BY rule_id, expression_id';
END test;
end;
/
create table emp (col1 int);
/
CREATE OR REPLACE type body test_body as
type t_emp is table of t_table index by varchar2(22);
emp_rec emp%ROWTYPE;
member PROCEDURE test(o_cursor OUT my_cursor)
IS
L_SQL varchar(20000) := '';
BEGIN
L_SQL := 'SELECT rule_id,
expression_id,
parent_expression_id,
operator
FROM emp
ORDER BY rule_id, expression_id';
OPEN o_cursor FOR L_SQL;
END test;
end;
/
-
ALTER TABLE … ADD …, ALTER TABLE/VIEW … SET SCHEMA …, ALTER DATABASE … CONVERT TO SCHEMA WITH PARENT … syntaxes are supported. All other syntaxes, such as ALTER TABLE … DELETE .. or ALTER TABLE … DROP … or ALTER TABLE … MODIFY … etc. are not supported.
-
Moving a table from one database/scheme to another is not supported through RENAME TABLE schema1.tableName1 TO schema2.tableName2.
-
Sequences are not taken into account and that is not a limitation but a choice because they have no effect on transactions nor Quality Rules
-
Oracle synonyms on packages are not taken into account.
-
For the QR 1101012 Specify column names instead of column numbers in ORDER BY clauses, the case when a function that returns a number or a numeric variable is used in order by is not reported to violate the rule.