Azure Java - 1.0
Extension ID
com.castsoftware.azure.java
What’s new?
See Azure Java 1.0 - Release Notes.
In what situation should you install this extension?
This extension should be used for analyzing java source code using any of the supported Azure services.
Azure Blob support
Whenever a call to a method carrying a CRUD operation on an Azure Blob is found in the source code, this extension evaluates the name of the container in which the operation is made and a link is created from the caller of the method to that blob container. The list of supported methods and the type of links created are listed in the following tables. If the evaluation of the container name fails (either due to missing information in the source code or to limitations in the evaluation) a link is created to an Unknown container.
For methods copying a blob from one container to another, a useSelectLink is created to the source container and both a useInsertLink and a useUpdateLink are created to the destination container.
Methods from Azure Storage Client library v. 12.x (com.azure.storage)
| Classes | Methods | link_types |
|---|---|---|
| com.azure.storage.blob.BlobServiceClient | deleteBlobContainer, deleteBlobContainerWithResponse | useDeleteLink |
| As above | undeleteBlobContainer, undeleteBlobContainerWithResponse | useUpdateLink |
| com.azure.storage.blob.BlobContainerClient | delete deleteWithResponse |
useDeleteLink |
| com.azure.storage.blob.specialized.BlobClientBase com.azure.storage.blob.specialized.BlobAsyncClientBase |
delete deleteWithResponse |
useDeleteLink |
| As above | download downloadContent downloadStream downloadContentWithResponse downloadStreamWithResponse downloadToFile downloadToFileWithResponse downloadWithResponse query queryWithResponse |
useSelectLink |
| As above | beginCopy copyFromUrl copyFromUrlWithResponse |
useSelectLink useInsertLink useUpdateLink |
| com.azure.storage.blob.BlobClient com.azure.storage.blob.BlobAsyncClient |
upload uploadFromFile uploadFromFileWithResponse uploadWithResponse |
useInsertLink useUpdateLink |
| com.azure.storage.blob.specialized.AppendBlobClient com.azure.storage.blob.specialized.AppendBlobAsyncClient |
appendBlock appendBlockWithResponse |
useUpdateLink |
| As above | appendBlockFromUrl appendBlockFromUrlWithResponse |
useSelectLink useInsertLink useUpdateLink |
| com.azure.storage.blob.specialized.BlockBlobClient com.azure.storage.blob.specialized.BlockBlobAsyncClient |
commitBlockList commitBlockListWithResponse |
useUpdateLink |
| As above | stageBlock | useInsertLink |
| As above | upload uploadWithResponse |
useInsertLink useUpdateLink |
| As above | stageBlockFromUrl stageBlockFromUrlWithResponse uploadFromUrl uploadFromUrlWithResponse |
useSelectLink useInsertLink useUpdateLink |
| com.azure.storage.blob.specialized.PageBlobClient com.azure.storage.blob.specialized.PageBlobAsyncClient |
clearPages clearPagesWithResponse |
useDeleteLink |
| As above | uploadPages uploadPagesWithResponse |
useInsertLink useUpdateLink |
| As above | copyIncremental copyIncrementalWithResponse uploadPagesFromUrl uploadPagesFromUrlWithResponse |
useSelectLink useInsertLink useUpdateLink |
| com.azure.storage.common.StorageOutputStream | write dispatchWrite writeInternal |
useUpdateLink |
| com.azure.storage.common.BlobInputStream | read | useSelectLink |
Methods form Azure Storage Client library v. 11.x (com.microsoft.azure.storage)
Note that the Azure Storage Client library v. 11.x is deprecated.
| Classes | Methods | link_types |
|---|---|---|
| com.microsoft.azure.storage.blob.CloudBlobContainer | delete deleteIfExists |
useDelete |
| com.microsoft.azure.storage.blob.CloudBlob | delete deleteIfExists |
useDelete |
| As above | download downloadRange downloadRangeInternal downloadRangeToByteArray downloadToByteArray downloadToFile |
useSelect |
| As above | upload uploadFromByteArray uploadFromFile |
useInsert useUpdate |
| As above | startCopy startCopyImpl |
useSelect useInsert useUpdate |
| com.microsoft.azure.storage.blob.CloudAppendBlob | append appendBlock appendFromByteArray appendFromFile appendText |
useUpdate |
| As above | upload | useInsert useUpdate |
| As above | appendBlockFromURI startCopy |
useSelect useInsert useUpdate |
| com.microsoft.azure.storage.blob.CloudBlockBlob | commitBlockList | useUpdate |
| As above | downloadBlockList downloadText |
useSelect |
| As above | upload uploadBlock uploadFromByteArray uploadFullBlob uploadText |
useInsert useUpdate |
| As above | createBlockFromURI startCopy |
useSelect useInsert useUpdate |
| com.microsoft.azure.storage.blob.CloudPageBlob | clearPages | useDelete |
| As above | downloadPageRanges | useSelect |
| As above | upload uploadFromByteArray uploadFromFile uploadPages |
useInsert useUpdate |
| As above | putPagesFromURI startCopy startIncrementalCopy |
useSelect useInsert useUpdate |
| com.microsoft.azure.storage.blob.BlobInputStream | read | useSelect |
| com.microsoft.azure.storage.blob.BlobOutputStream | write | useUpdate |
Example
When analyzing the following source code:
import com.azure.storage.blob.BlobServiceClient;lt text
import com.azure.storage.blob.BlobContainerClient;
import com.azure.storage.blob.specialized.BlockBlobClient;
public class BasicExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
StorageSharedKeyCredential credential = new StorageSharedKeyCredential(accountName, accountKey);
String endpoint = String.format(Locale.ROOT, "https://%s.blob.core.windows.net", accountName);
BlobServiceClient storageClient = new BlobServiceClientBuilder().endpoint(endpoint).credential(credential).buildClient();
BlobContainerClient blobContainerClient = storageClient.getBlobContainerClient("mycontainer");
blobContainerClient.create();
BlockBlobClient blobClient = blobContainerClient.getBlobClient("HelloWorld.txt").getBlockBlobClient();
blobClient.upload(dataStream, data.length());
}
}
we get the following result:
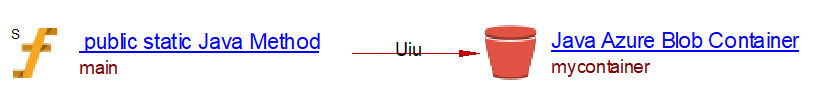
Azure Service Bus support
Whenever a call to a method carrying a sender/receiver operation on an Azure Service Bus queue/topic is found in the source code, this extension evaluates the name of the queue/topic in which the operation is made and a link is created from the caller of the method to that Service Bus Publisher/Receiver. If the evaluation of the Service Bus queue/topic name fails (either due to missing information in the source code or to limitations in the evaluation) a link is created to an Unknown Service Bus Publisher/Receiver.
This extension supports:
- the package Azure Messaging Service Bus client API (latest), current version 7.9.1
- the package Azure Service Bus client API (legacy), current version 3.6.6.
Supported APIs
com.azure.messaging.servicebus
For the publisher side:
| Supported API methods (com.azure.messaging.servicebus) | Object created (Callee) | Link created | Link created |
|---|---|---|---|
| ServiceBusSenderClient.sendMessage | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| ServiceBusSenderClient.sendMessages | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| ServiceBusSenderAsyncClient.sendMessage | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| ServiceBusSenderAsyncClient.sendMessages | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
For the receiver side:
| Supported API methods (com.azure.messaging.servicebus) | Object created (Caller) | Link created | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
ServiceBusReceiverClient.receiveMessages |
Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| ServiceBusProcessorClient.start | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Receiver |
callLink | Java Method |
ServiceBusReceiverAsyncClient (reactor.core.publisher.Flux.subscribe) ServiceBusSessionReceiverAsyncClient |
Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Receiver |
callLink |
Java Lambda Expression /Java Method (see also Limitation section below) |
com.microsoft.azure.servicebus
For the publisher side:
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.servicebus) | Object created (Callee) | Link created | Caller type |
|---|---|---|---|
| QueueClient.scheduleMessage | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| QueueClient.scheduleMessageAsync | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| QueueClient.send | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| QueueClient.sendAsync | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| QueueClient.sendBatch | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| QueueClient.sendBatchAsync | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| TopicClient.scheduleMessage | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| TopicClient.scheduleMessageAsync | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| TopicClient.send | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| TopicClient.sendAsync | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| TopicClient.sendBatch | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| TopicClient.sendBatchAsync | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
For the receiver side:
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.servicebus) | Object created (Caller) | Link created | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| QueueClient.registerMessageHandler | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| QueueClient.registerSessionHandler | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| SubscriptionClient.registerMessageHandler | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| SubscriptionClient.registerSessionHandler | Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
Code samples
package com.foo.test;
import com.azure.messaging.servicebus.ServiceBusSenderClient;
import com.azure.messaging.servicebus.ServiceBusReceiverClient;
import com.azure.messaging.servicebus.ServiceBusClientBuilder;
import com.azure.messaging.servicebus.ServiceBusMessage;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
//
// https://docs.microsoft.com/fr-fr/azure/service-bus-messaging/service-bus-java-how-to-use-queues
//
public class SendReceive {
static String connectionString = "<NAMESPACE CONNECTION STRING>";
static String queueName = "<QUEUE NAME>";
static void sendMessage() {
// create a Service Bus Sender client for the queue
ServiceBusSenderClient senderClient = new ServiceBusClientBuilder()
.connectionString(connectionString)
.sender()
.queueName(queueName)
.buildClient();
// send one message to the queue
senderClient.sendMessage(new ServiceBusMessage("Hello, World!"));
System.out.println("Sent a single message to the queue: " + queueName);
}
static void receiveMessages() {
ServiceBusReceiverClient receiverClient = new ServiceBusClientBuilder()
.connectionString(connectionString)
.receiver()
.queueName(queueName)
.buildClient();
// Use the receiver and finally close it.
receiverClient.receiveMessages(1);
receiverClient.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
sendMessage();
receiveMessages();
}
}

Azure Functions support
Azure Functions allow executing some source code on the cloud. The execution can be set to be triggered by some Azure events. In Java, the Azure Functions API are defined using annotations: com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation:
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation) | Object created (Caller) | Link created | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| @FunctionName | Java Azure (Unknown) Function | callLink | Java Method |
The analyzer will create a Java Azure Function object with a call link to the handler of the Azure Function.
@FunctionName("RetrieveDailySubscriptions")
public void retrieveDailySubscriptions(...
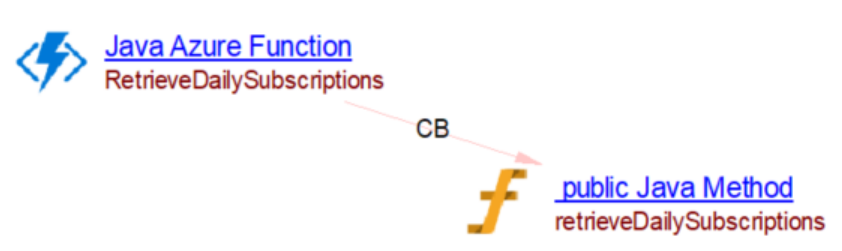
The Azure Function can be configured to be triggered or to interact with some other Azure services. Triggers cause a function to run. Binding to a function is a way of declaratively connecting another resource to the function; bindings may be connected as input bindings, output bindings, or both. Data from bindings is provided to the function as parameters. The following table list the supported interactions:
| Service | trigger | input | output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Http | - | - | |
| Service Bus | - | ||
| Blob | |||
| CosmosDB | |||
| Event Hubs | - |
Detailed support for each of these interactions is given in the following sections.
Support for binding with Azure Service Bus
Service Bus can be used as a trigger or as an output binding for Azure function. For the trigger, we create a Java Azure Service Bus Receiver object with a call link to Java Azure Function object. For output binding, the Java function sends a message to a Topic or a Queue. We create a Java Azure Service Bus Publisher object with a callLink to that object from the handler of function.
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation) | Object created (Caller) | Link created | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
@ServiceBusQueueTrigger @ServiceBusTopicTrigger |
Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Receiver | callLink | Java Azure Function |
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation) | Object created (Callee) | Link created | Caller type |
|---|---|---|---|
@ServiceBusQueueOutput @ServiceBusTopicOutput |
Java Azure (Unknown) Service Bus Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
For example, when analyzing the following source code:
@FunctionName("RetrieveDailySubscriptions")
public void retrieveDailySubscriptions(
@TimerTrigger(
name = "timer",
schedule = "0 0 0 * * *") String timerInfo,
@ServiceBusQueueOutput(name = "sb",
queueName = "%PaymentQueue%",
connection = "ServiceBusConnectionStr") OutputBinding<Subscription[]> subscriptionOutput,
final ExecutionContext context) {
subscriptionOutput.setValue(subscriptions);
}
@FunctionName("ProcessSubscriptionPayment")
public void processSubscriptionPayment(
@ServiceBusQueueTrigger(
name = "sb",
queueName = "%PaymentQueue%",
connection = "ServiceBusConnectionStr") Subscription subscription,
final ExecutionContext context) {
}
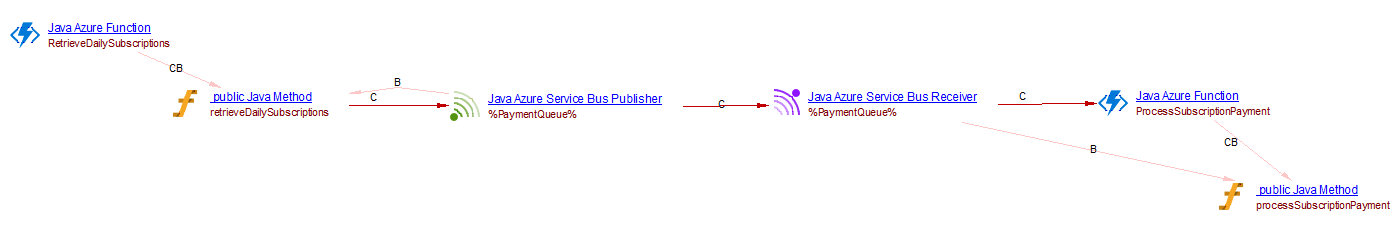
HttpTrigger
We create operations linked to the handler of function. If the type of operation is not specified, the function responds to all HTTP methods, we create Java Azure Any Operation. If the url is not specified, it is the function name:
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation) | Object created (Caller) | Link created | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
@HttpTrigger |
Java Azure Get Operation Java Azure Post Operation Java Azure Put Operation Java Azure Delete Operation Java Azure Any Operation |
callLink | Java Azure Function |
For example, when analyzing the following source code:
@FunctionName("ServiceBusTopicOutput")
public void serviceBusTopicOutput(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req", methods = {HttpMethod.GET, HttpMethod.POST}, authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS) HttpRequestMessage<Optional<String>> request,
@ServiceBusTopicOutput(name = "message", topicName = "%SBTopicName%", subscriptionName = "%SBTopicSubName%", connection = "AzureWebJobsServiceBus") OutputBinding<String> output,
final ExecutionContext context
) {
String message = request.getBody().orElse("default message");
output.setValue(message);
context.getLogger().info("Java Service Bus Topic output function got a message: " + message);
}
you will get the following result:
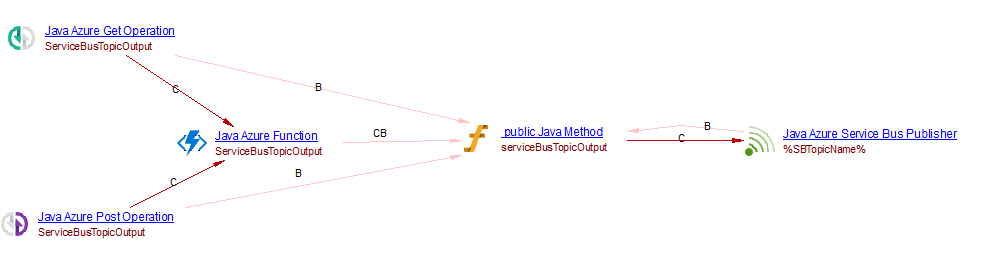
Durable functions
Durable Functions allow calling an azure function from another Azure Function:
Supported API methods (com.microsoft.durabletask) |
Object created (Callee) | Link created | Caller |
|---|---|---|---|
DurableTaskClient.scheduleNewOrchestrationInstance TaskOrchestrationContext.callSubOrchestrator TaskOrchestrationContext.callActivity |
Java Call to Azure (Unknown) Function | callLink | JV Method |
The extension com.castsoftware.wbslinker will match Java Call to Azure Function objects to Azure Function objects such as Java Azure Function. For example, when analyzing the following source code:
@FunctionName("StartHelloCities")
public HttpResponseMessage startHelloCities(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req", methods = {HttpMethod.POST}) HttpRequestMessage<Optional<String>> req,
@DurableClientInput(name = "durableContext", taskHub = "%MyTaskHub%") DurableClientContext durableContext,
final ExecutionContext context) {
DurableTaskClient client = durableContext.getClient();
String instanceId = client.scheduleNewOrchestrationInstance("HelloCities");
context.getLogger().info("Created new Java orchestration with instance ID = " + instanceId);
return durableContext.createCheckStatusResponse(req, instanceId);
}
/
* This is the orchestrator function, which can schedule activity functions, create durable timers,
* or wait for external events in a way that's completely fault-tolerant. The OrchestrationRunner.loadAndRun()
* static method is used to take the function input and execute the orchestrator logic.
*/
@FunctionName("HelloCities")
public String helloCitiesOrchestrator(@DurableOrchestrationTrigger(name = "runtimeState") String runtimeState) {
return OrchestrationRunner.loadAndRun(runtimeState, ctx -> {
String result = "";
result += ctx.callActivity("SayHello", "Tokyo", String.class).await() + ", ";
result += ctx.callActivity("SayHello", "London", String.class).await() + ", ";
result += ctx.callActivity("SayHello", "Seattle", String.class).await();
return result;
});
}
/
* This is the activity function that gets invoked by the orchestrator function.
*/
@FunctionName("SayHello")
public String sayHello(@DurableActivityTrigger(name = "name") String name) {
return String.format("Hello %s!", name);
}
you will get the following result:
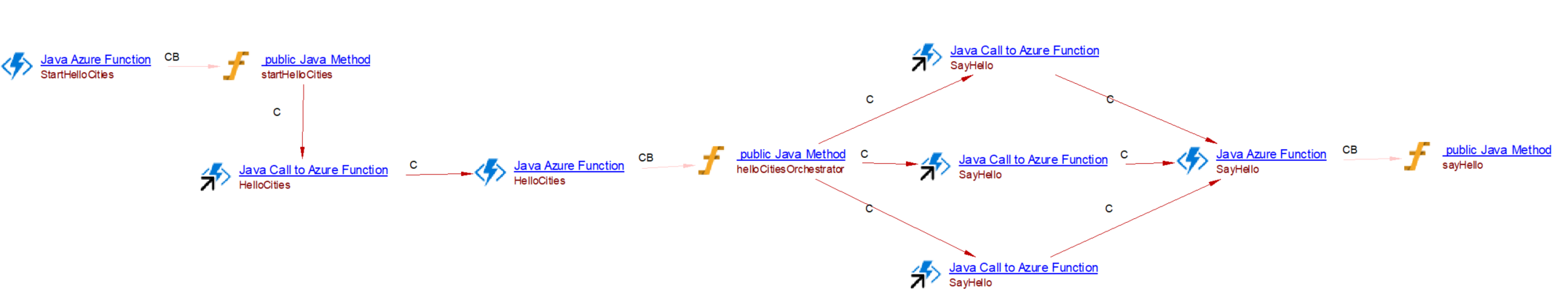
Durable function client with HTTP trigger
It is common that a durable function client is triggered by an HTTP call and that with a proper URL any orchestrator function can be triggered. In this case, for each existing orchestrator azure function, an Operation with the corresponding url is created with a callLink to a Call to Azure Function object to the orchestrator function. For example when analyzing the following code:
@FunctionName("HttpStart")
public HttpResponseMessage httpStart(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req", route = "orchestrators/{functionName}") HttpRequestMessage<?> req,
@DurableClientInput(name = "durableContext") DurableClientContext durableContext,
@BindingName("functionName") String functionName,
final ExecutionContext context) {
DurableTaskClient client = durableContext.getClient();
String instanceId = client.scheduleNewOrchestrationInstance(functionName);
context.getLogger().info("Created new Java orchestration with instance ID = " + instanceId);
return durableContext.createCheckStatusResponse(req, instanceId);
}
if your source code contains two orchestrator azure functions named HelloCities and HelloCities2, you will get the following result:
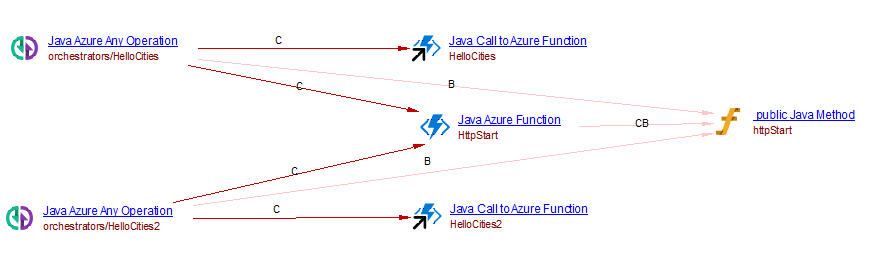
Binding with Azure Blob
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation) | Link created | Caller type | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| @BlobTrigger | callLink | Java Method | Java Azure function |
| @BlobInput | useSelectLink | Java Method | Java Azure Blob Container |
| @BlobOutput | useUpdateLink | Java Method | Java Azure Blob Container |
Blob trigger - @BlobTrigger
Whenever a file is added or updated to a blob container the azure function will be executed. We add the property ‘CAST_Azure_Function.blob_triggers’ to the Java Azure function. The extension com.castsoftware.wbslinker will create a callLink from the method (which added or updated to the blob) to the Java Azure function. For example, when analyzing the following source code,
@FunctionName("blobprocessor")
public void run(
@BlobTrigger(name = "file",
dataType = "binary",
path = "myblob/{name}",
connection = "MyStorageAccountAppSetting") byte[] content,
@BindingName("name") String filename,
final ExecutionContext context
) {
context.getLogger().info("Name: " + filename + " Size: " + content.length + " bytes");
}
you will get the following result:
Input Binding - @BlobInput
This is used to get access to a blob. From a Java Method, we create a useSelectLink to the blob object. For example, when analyzing the following source code:
@FunctionName("getBlobSizeHttp")
@StorageAccount("Storage_Account_Connection_String")
public HttpResponseMessage blobSize(
@BlobInput(
name = "file",
dataType = "binary",
path = "samples-workitems/{Query.file}")
byte[] content,
final ExecutionContext context) {
}
you will get the following result:

Output Binding - @BlobOutput
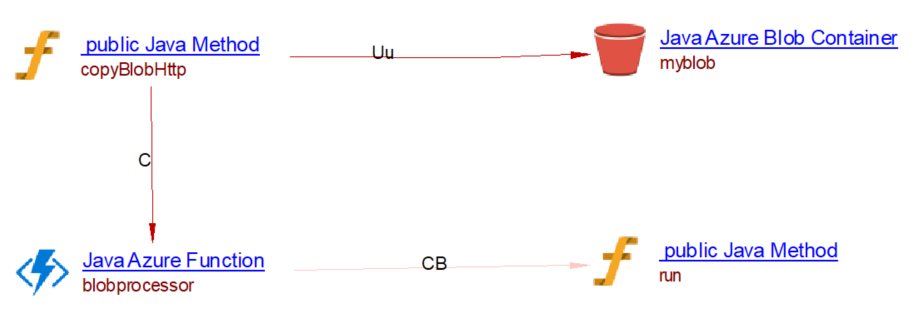
This is used to update a blob. From a Java Method, we create a useUpdateLink to the blob object. For example, when analyzing the following source code:
@FunctionName("copyBlobHttp")
@StorageAccount("Storage_Account_Connection_String")
public HttpResponseMessage copyBlobHttp(
@BlobOutput(
name = "target",
path = "myblob/{Query.file}-CopyViaHttp")
OutputBinding<String> outputItem,
final ExecutionContext context) {
}
you will get the following result:

Binding with CosmosDB
Supported for Java from function 2.x and higher:
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation) | Link created | Caller type | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| @CosmosDBTrigger | callLink | Java Method | Java Azure function |
| @CosmosDBInput | useSelectLink | Java Method | Java CosmosDB Collection |
| @CosmosDBOutput | useUpdateLink | Java Method | Java CosmosDB Collection |
CosmosDB trigger - @CosmosDBTrigger
An Azure Function is invoked when there are inserts or updates in the specified database and collection. We add the property ‘CAST_Azure_Function.cosmosDB_triggers’ to the azure function. The extension com.castsoftware.wbslinker will create a callLink from the JV method (which added or updated to the cosmosDB) to the azure function. For example, when analyzing the following source code:
@FunctionName("CosmosTriggerAndOutput")
public void CosmosTriggerAndOutput(
@CosmosDBTrigger(name = "itemIn", databaseName = "familydb", collectionName = "familycoll", leaseCollectionName = "leases", connectionStringSetting = "AzureWebJobsCosmosDBConnectionString", createLeaseCollectionIfNotExists = true) Object inputItem,
final ExecutionContext context) {
context.getLogger().info("Java Cosmos DB trigger function executed. Received document: " + inputItem);
}
you will get the following result:
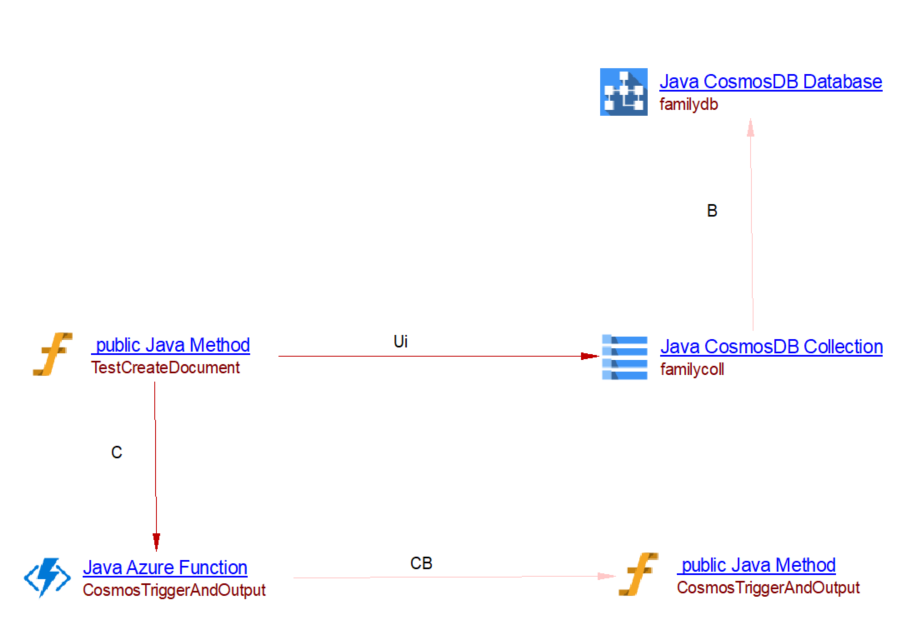
Input Binding - @CosmosDBInput
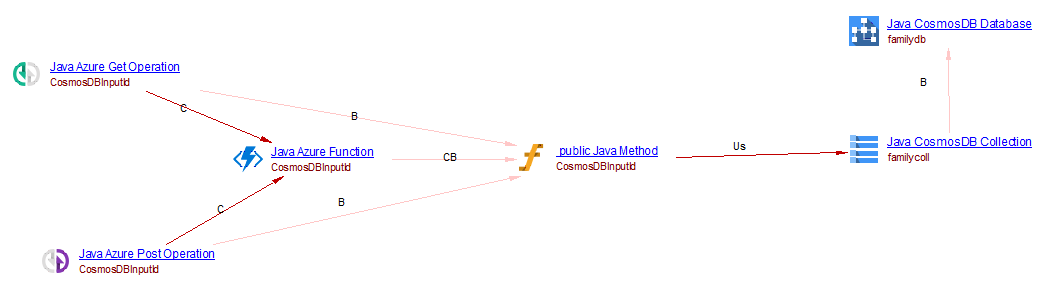
This is used to get access to CosmosDB database and collection. From a Java Method (which is the handler of the azure function), we create a useSelectLink to the CosmosDB collection object. For example, when analyzing the following source code:
@FunctionName("CosmosDBInputId")
public HttpResponseMessage CosmosDBInputId(@HttpTrigger(name = "req", methods = { HttpMethod.GET,
HttpMethod.POST }, authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS) HttpRequestMessage<Optional<String>> request,
@CosmosDBInput(name = "item", databaseName = "familydb", collectionName = "familycoll", connectionStringSetting = "AzureWebJobsCosmosDBConnectionString", id = "{docId}") String item,
final ExecutionContext context) {
context.getLogger().info("Java HTTP trigger processed a request.");
if (item != null) {
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.OK).body("Received Document" + item).build();
} else {
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body("Did not find expected item in ItemsCollectionIn").build();
}
}
you will get the following result:
Output Binding - @CosmosDBOutput
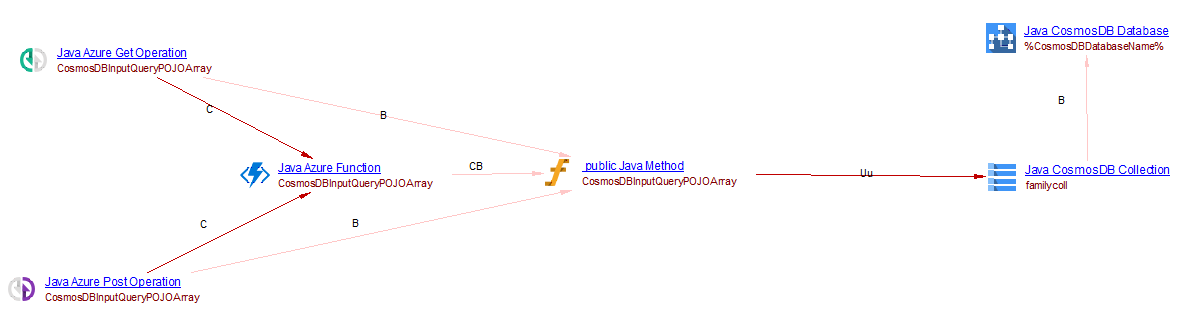
This is used to update a CosmosDB database and collection. From a Java Method (which is the handle of the azure function), we create a useUpdateLink to the CosmosDB collection object. For example, when analyzing the following source code:
@FunctionName("CosmosDBInputQueryPOJOArray")
public HttpResponseMessage CosmosDBInputQueryPOJOArray(@HttpTrigger(name = "req", methods = { HttpMethod.GET,
HttpMethod.POST }, authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS) HttpRequestMessage<Optional<String>> request,
@CosmosDBOutput(name = "itemsOut", databaseName = "%CosmosDBDatabaseName%", collectionName = "familycoll", connectionStringSetting = "AzureWebJobsCosmosDBConnectionString") OutputBinding<Document[]> itemsOut,
final ExecutionContext context) {
context.getLogger().info("Java HTTP trigger processed a request.");
}
you will get the following result:
Support Azure Event Hubs Trigger and Binding Output
Event Hubs can be used as a trigger or as an output binding for Azure function. For the trigger, we create a Java Azure Event Hub Receiver object with a call link to Java Azure function object. For output binding, the Java function sends events to a Event Hub. We create a Java Azure Event Hub Publisher object with a callLink to that object from the handler of function.
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation) | Object created (Caller) | Link created | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| @EventHubTrigger | Java Azure Event Hub Receiver / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver | callLink | Java Azure function |
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation) | Object created (Callee) | Link created | Caller type |
|---|---|---|---|
| @EventHubOutput | Java Azure Event Hub Publisher / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
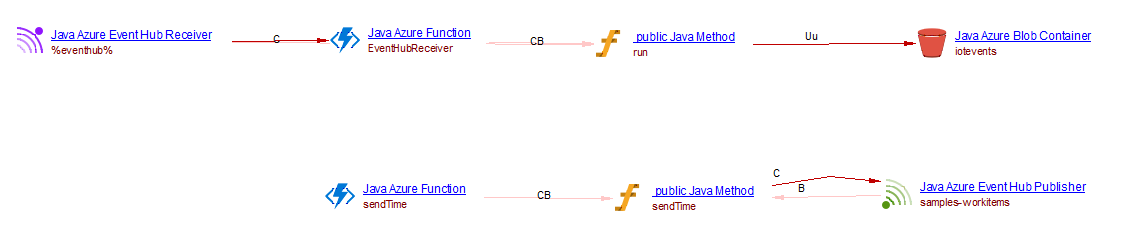
For example, when analyzing the following source code:
@FunctionName("EventHubReceiver")
@StorageAccount("bloboutput")
public void run(
@EventHubTrigger(name = "message",
eventHubName = "%eventhub%",
consumerGroup = "%consumergroup%",
connection = "eventhubconnection",
cardinality = Cardinality.ONE)
String message,
final ExecutionContext context,
@BindingName("Properties") Map<String, Object> properties,
@BindingName("SystemProperties") Map<String, Object> systemProperties,
@BindingName("PartitionContext") Map<String, Object> partitionContext,
@BindingName("EnqueuedTimeUtc") Object enqueuedTimeUtc,
@BlobOutput(
name = "outputItem",
path = "iotevents/{datetime:yy}/{datetime:MM}/{datetime:dd}/{datetime:HH}/" +
"{datetime:mm}/{PartitionContext.PartitionId}/{SystemProperties.SequenceNumber}.json")
OutputBinding<String> outputItem) {
var et = ZonedDateTime.parse(enqueuedTimeUtc + "Z"); // needed as the UTC time presented does not have a TZ
// indicator
context.getLogger().info("Event hub message received: " + message + ", properties: " + properties);
context.getLogger().info("Properties: " + properties);
context.getLogger().info("System Properties: " + systemProperties);
context.getLogger().info("partitionContext: " + partitionContext);
context.getLogger().info("EnqueuedTimeUtc: " + et);
outputItem.setValue(message);
}
@FunctionName("sendTime")
@EventHubOutput(name = "event", eventHubName = "samples-workitems", connection = "AzureEventHubConnection")
public String sendTime(
@TimerTrigger(name = "sendTimeTrigger", schedule = "0 */5 * * * *") String timerInfo) {
return LocalDateTime.now().toString();
}
you will get the following result:
Azure Event Hubs support
Whenever a call to a method carrying a sender/receiver operation on an Azure Event Hubs is found in the source code, this extension evaluates the name of the Event Hub in which the operation is made and a link is created from the caller of the method to that Event Hub Publisher/Receiver. If the evaluation of the Event Hub name fails (either due to missing information in the source code or to limitations in the evaluation) a link is created to an Unknown Event Hub Publisher/Receiver.
This extension supports:
- the package azure-messaging-eventhubs (latest), current version 5.14.0
- the packages azure-eventhubs and azure-eventhubs-eph (legacy), current version 3.3.0
Supported send/receive Events APIs
com.azure.messaging.eventhubs (latest)
For the publisher side (Send Events):
| Supported API methods (com.azure.messaging.eventhubs) | Object created (Callee) | Link created | Caller type |
|---|---|---|---|
| EventHubProducerClient.send | Java Azure Event Hub Publisher / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| EventHubProducerAsyncClient.send | Java Azure Event Hub Publisher / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
For the receiver side (Receive Events):
| Supported API methods (com.azure.messaging.eventhubs) | Object created (Caller) | Link created | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| EventHubConsumerClient.receiveFromPartition | Java Azure Event Hub Receiver / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| EventHubConsumerAsyncClient.receiveFromPartition | Java Azure Event Hub Receiver / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| EventHubConsumerAsyncClient.receive | Java Azure Event Hub Receiver / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| EventProcessorClient.start | Java Azure Event Hub Receiver / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
com.microsoft.azure.eventprocessorhost (legacy)
For the publisher side (Send Events):
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.eventhubs) | Object created (Callee) | Link created | Caller type |
|---|---|---|---|
| EventHubClient.send | Java Azure Event Hub Publisher / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| EventHubClient.sendsync | Java Azure Event Hub Publisher / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| PartitionSender.send | Java Azure Event Hub Publisher / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
| PartitionSender.sendsync | Java Azure Event Hub Publisher / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Publisher | callLink | Java Method |
For the receiver side (Receive Events):
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.eventhubs) | Object created (Caller) | Link created | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| PartitionReceiver.receive | Java Azure Event Hub Receiver / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| PartitionReceiver.receiveSync | Java Azure Event Hub Receiver / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.eventprocessorhost) | Object created (Caller) | Link created | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| EventProcessorHost.registerEventProcessor | Java Azure Event Hub Receiver / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
| EventProcessorHost.registerEventProcessorFactory | Java Azure Event Hub Receiver / Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver | callLink | Java Method |
The extension com.castsoftware.wbslinker will match Azure Event Hub Publisher objects to Azure Event Hub Receiver.
Checkpoint Store
We support Azure Event Hubs Checkpoint Store using Storage Blobs
| Supported API methods (com.azure.messaging.eventhubs) | Link created | Caller type | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| EventProcessorClientBuilder.checkpointStore | useUpdateLink | Java Method | Java Azure Blob Container |
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.azure.eventprocessorhost) | Link created | Caller type | Callee type |
|---|---|---|---|
| EventProcessorHost.EventProcessorHostBuilder.useAzureStorageCheckpointLeaseManager | useUpdateLink | Java Method | Java Azure Blob Container |
From a Java Method, we create a useUpdateLink to the blob container object. For example, when analyzing the following source code:
public class Sender {
private static final String connectionString = "<Event Hubs namespace connection string>";
private static final String eventHubName = "<Event hub name>";
public static void main(String[] args) {
publishEvents();
}
/
* Code sample for publishing events.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the EventData is bigger than the max batch size.
*/
public static void publishEvents() {
// create a producer client
EventHubProducerClient producer = new EventHubClientBuilder()
.connectionString(connectionString, eventHubName)
.buildProducerClient();
// sample events in an array
List<EventData> allEvents = Arrays.asList(new EventData("Foo"), new EventData("Bar"));
// create a batch
EventDataBatch eventDataBatch = producer.createBatch();
for (EventData eventData : allEvents) {
// try to add the event from the array to the batch
if (!eventDataBatch.tryAdd(eventData)) {
// if the batch is full, send it and then create a new batch
producer.send(eventDataBatch);
eventDataBatch = producer.createBatch();
// Try to add that event that couldn't fit before.
if (!eventDataBatch.tryAdd(eventData)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Event is too large for an empty batch. Max size: "
+ eventDataBatch.getMaxSizeInBytes());
}
}
}
// send the last batch of remaining events
if (eventDataBatch.getCount() > 0) {
producer.send(eventDataBatch);
}
producer.close();
}
}
and:
public class Receiver {
private static final String connectionString = "<Event Hubs namespace connection string>";
private static final String eventHubName = "<Event hub name>";
private static final String storageConnectionString = "<Storage connection string>";
private static final String storageContainerName = "<Storage container name>";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Create a blob container client that you use later to build an event processor client to receive and process events
BlobContainerAsyncClient blobContainerAsyncClient = new BlobContainerClientBuilder()
.connectionString(storageConnectionString)
.containerName(storageContainerName)
.buildAsyncClient();
// Create a builder object that you will use later to build an event processor client to receive and process events and errors.
EventProcessorClientBuilder eventProcessorClientBuilder = new EventProcessorClientBuilder()
.connectionString(connectionString, eventHubName)
.consumerGroup(EventHubClientBuilder.DEFAULT_CONSUMER_GROUP_NAME)
.processEvent(PARTITION_PROCESSOR)
.processError(ERROR_HANDLER)
.checkpointStore(new BlobCheckpointStore(blobContainerAsyncClient));
// Use the builder object to create an event processor client
EventProcessorClient eventProcessorClient = eventProcessorClientBuilder.buildEventProcessorClient();
System.out.println("Starting event processor");
eventProcessorClient.start();
System.out.println("Press enter to stop.");
System.in.read();
System.out.println("Stopping event processor");
eventProcessorClient.stop();
System.out.println("Event processor stopped.");
System.out.println("Exiting process");
}
public static final Consumer<EventContext> PARTITION_PROCESSOR = eventContext -> {
PartitionContext partitionContext = eventContext.getPartitionContext();
EventData eventData = eventContext.getEventData();
System.out.printf("Processing event from partition %s with sequence number %d with body: %s%n",
partitionContext.getPartitionId(), eventData.getSequenceNumber(), eventData.getBodyAsString());
// Every 10 events received, it will update the checkpoint stored in Azure Blob Storage.
if (eventData.getSequenceNumber() % 10 == 0) {
eventContext.updateCheckpoint();
}
};
public static final Consumer<ErrorContext> ERROR_HANDLER = errorContext -> {
System.out.printf("Error occurred in partition processor for partition %s, %s.%n",
errorContext.getPartitionContext().getPartitionId(),
errorContext.getThrowable());
};
}
you will get the following result:

Azure SignalR service support
Client side
Call methods that run on the server. When there is an API method which invokes a hub method, we create a Java Azure SignalR Call to Hub Method* *object where the object name is the name of invoked hub method. Add a property *hub_Name *to save the hub name which is connected by this client.
| Supported API methods (com.microsoft.signalr) | Object created | Link created | Caller type |
|---|---|---|---|
HubConnection.send HubConnection.start HubConnection.stop |
Java Azure SignalR Call to Hub Method / Java Azure SignalR Call to Unknown Hub Method |
callLink |
Java Method |
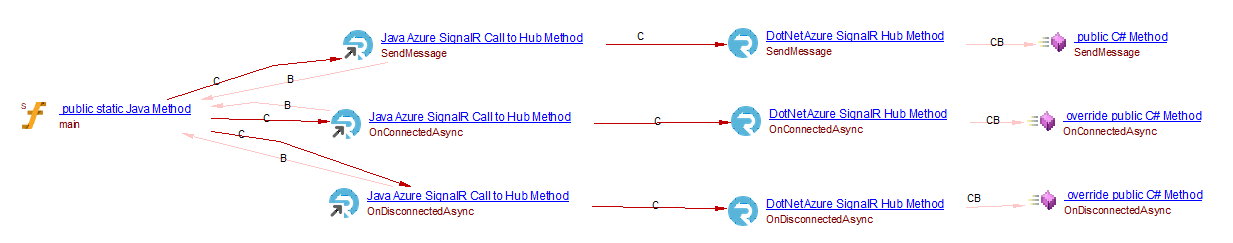
The extension com.castsoftware.wbslinker will match Java Azure SignalR Call to Hub Method objects to DotNet Azure SignalR Hub Method in server side (which created by Azure Dotnet extension). For example, when analyzing the following source code in client side:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HubConnection hubConnection = HubConnectionBuilder.create("/chatHub")
.build();
...
//This is a blocking call
hubConnection.start().blockingAwait();
while (!input.equals("leave")){
input = reader.nextLine();
hubConnection.send("SendMessage", input);
}
hubConnection.stop();
}
and if your source code contains a corresponding signalR Hub class, you will get the following result:
Objects
The following objects are resolved:
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
|
Java Azure Blob Container |
|
Java Azure Unknown Blob Container |
|
Java Azure Service Bus Publisher |
|
Java Azure Service Bus Receiver |
|
Java Azure Unknown Service Bus Publisher |
|
Java Azure Unknown Service Bus Receiver |
|
Java Azure Function |
|
Java Azure Unknown Function |
|
Java Call to Azure Function |
|
Java Call to Azure Unknown Function |
|
Java Azure Get Operation |
|
Java Azure Post Operation |
|
Java Azure Put Operation |
|
Java Azure Delete Operation |
|
Java Azure Any Operation |
|
Java Azure Event Hub Publisher |
|
Java Azure Event Hub Receiver |
|
Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Publisher |
|
Java Azure Unknown Event Hub Receiver |
|
Java Azure SignalR Call to Hub Method |
|
Java Azure SignalR Call to Unknown Hub Method |
Known limitations
- In Service Bus support, for the support of com.azure.messaging.servicebus.ServiceBusReceiverAsyncClient (reactor.core.publisher.Flux.subscribe), if the first parameter of method reactor.core.publisher.Flux.subscribe is a method reference (utilize the ::operator), the callLink do not point to this method reference but its parent.