GCP Pub Sub support for Node.js
Introduction
Google Cloud Platform Pub/Sub is a messaging service in the cloud that can be used to publish and subscribe to events. CAST supports only the API methods relevant for the modelization of message publishing, topic subscription, and message reception.
Objects
This extension, when the Node.js client library for Google Pub/Sub is found in the source code, may create the following objects representing message publishers, topic subscriptions and message receivers:
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
 |
NodeJS GCP Pub/Sub Publisher |
 |
NodeJS GCP Unknown Pub/Sub Publisher |
 |
NodeJS GCP Pub/Sub Subscription |
 |
NodeJS GCP Pub/Sub Receiver |
 |
NodeJS GCP Unknown Pub/Sub Receiver |
When the name of a created or just referred subscription in the code is not resolved, an Unknown Receiver object will be created with name Unknown. In this case no subscription object is created. However, when topics are not resolved for a well resolved subscription name, a Subscription object will be created with an empty topics property.
The com.castsoftware.wbslinker extension* *is responsible for matching Publisher/Subscription/Receiver objects between different technologies according to the name/property matching protocol. Note that Unknown objects are not considered in this linking protocol.
API methods
Publisher
The supported “publish” API methods are:
| API method | Object created | Link from caller |
|---|---|---|
| Topic.publish | NodeJS GCP (Unknown) Pub/Sub Publisher | callLink |
| Topic.publishJSON | NodeJS GCP (Unknown) Pub/Sub Publisher | callLink |
| Topic.publishMessage | NodeJS GCP (Unknown) Pub/Sub Publisher | callLink |
| Topic.resumePublishing | NodeJS GCP (Unknown) Pub/Sub Publisher | callLink |
| PublisherClient.publish | NodeJS GCP (Unknown) Pub/Sub Publisher | callLink |
When one of the supported API methods for message publishing is found, this extension evaluates the topic name and creates a NodeJS GCP Pub/Sub Publisher named as the topic. When the topic name cannot be resolved, an Unknown Publisher object is created named Unknown.
Receiver
The supported “reception” API methods are:
| API method | Object created | Link to handler (if resolved) from Receiver | Handler | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subscription.on | NodeJS GCP (Unknown) Pub/Sub Receiver | callLink | Callback method passed as argument. | Only object created when first parameter is equal to ‘message’. |
| SubscriberClient.pull | NodeJS GCP (Unknown) Pub/Sub Receiver | callLink | Parent of the object calling the API method | |
| SubscriberClient.streamingPull | NodeJS GCP Unknown Pub/Sub Receiver | callLink | Parent of the object calling the API method | Limited support: only Unknown objects are created because of complexity to analyze this low-level API. |
| SubscriberClient.subscriptionPath | N/A | N/A | N/A | Method used to provide subscription ids to the pull request. N/A: Not applicable. |
When one of the supported API methods for message reception is found, this extension evaluates the subscription name and creates a NodeJS GCP Pub/Sub Receiver named as the subscription. When the subscription name cannot be resolved, an Unknown Receiver object is created named Unknown.
Subscription
The supported “subscription” API methods are:
| API method | Object created | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Topic.subscription | NodeJS GCP Pub/Sub Subscription | Contains a list of topics in “Topics subscribed to” property. |
| Topic.createSubscription | NodeJS GCP Pub/Sub Subscription | As above |
| PubSub.subscription | NodeJS GCP Pub/Sub Subscription | As above |
| PubSub.createSubscription | NodeJS GCP Pub/Sub Subscription | As above |
When the subscription name is not resolved, no object is created. Certain APIs for reception (such as SubscriberClient.pull) can rely on subscription names but do not require topic names. In that case no Subscription object is created. Indeed the subscription object is expected to be created in a different place (possibly with a different language).
Topic evaluation
For topic evaluation, both for Subscriptions and Publishers, the following API methods are supported:
| API methods | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Pubsub.createTopic | Used for evaluation of publishing/subscription topics. |
| PubSub.topic | As above |
| PublisherClient.topicPath | As above |
Example
The JavaScript code below publishes a message on topic my-topic:
const {PubSub} = require('@google-cloud/pubsub');
const pubsub = new PubSub();
const topic = pubsub.topic('my-topic');
const data = Buffer.from('Hello, world!');
const callback = (err, messageId) => {
if (err) {
// Error handling omitted.
}
};
topic.publishMessage({data}, callback); // this results in a Publisher object
The code below shows a subscription to the same my-topic topic and the reception of the messages via the Subscription.on() API method:
const {PubSub} = require('@google-cloud/pubsub');
const pubsub = new PubSub();
const topic = pubsub.topic('my-topic2');
const subscription = topic.subscription('my-subscription2'); // this results in a Subscription object
const callback = function(message) {};
subscription.on('message', callback); // this results in a Receiver object and the link to the callback function
The resulting objects created by the Node.js extension are shown below with the respective links from the JavaScript caller to the CPG Pub/Sub Publisher and from the GCP Pub/Sub Receiver to the callback function (NONAME):
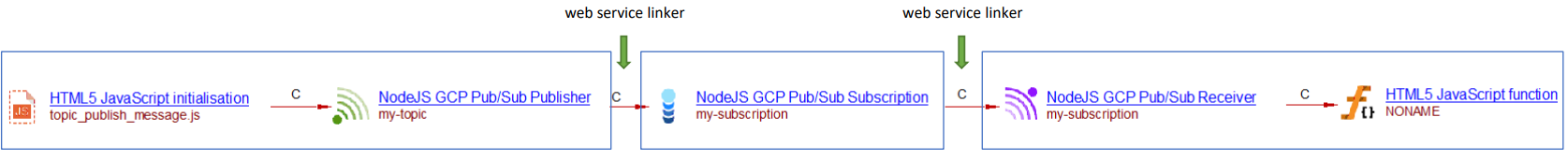
The synchronicity of the links from JavaScript to Publisher and from Receiver to JavaScript objects will be denoted by the property “Is the call asynchronous”. Note that a call to an asynchronous API with an await is considered as a synchronous call. The links between Publisher/Subscription/Receiver objects are create during the application-level analysis step, even in the case they pertain to the same technology as in the present example.